Jump to section
Food Standards Agency - Alerts Analysis
![]()
Last Updated: Wednesday, January 28, 2026 09:15 AM - Data up to Tuesday, 27 January, 2026
Pathogen Analysis for Food Safety Alerts from food.gov.uk
Food safety alerts are an essential tool for protecting public health, as they enable swift action to be taken in response to potential threats. In the UK, the Food Standards Agency (FSA) is responsible for issuing food safety alerts to inform consumers and industry stakeholders of potential risks associated with certain foods or products. These alerts are critical for ensuring that contaminated or potentially harmful products are removed from the market as quickly as possible, thereby minimizing the risk of foodborne illness outbreaks.
This section of the analysis focuses on a comprehensive review of food safety alerts issued by the FSA with a specific emphasis on pathogenic organisms such as Salmonella, Listeria, Campylobacter, and E. coli. By examining these data, this study aims to assess the effectiveness of the current alert system in detecting and responding to outbreaks, identify trends and patterns in the types of pathogens involved, and provide insights that can inform strategies for improving food safety and reducing public health risks.
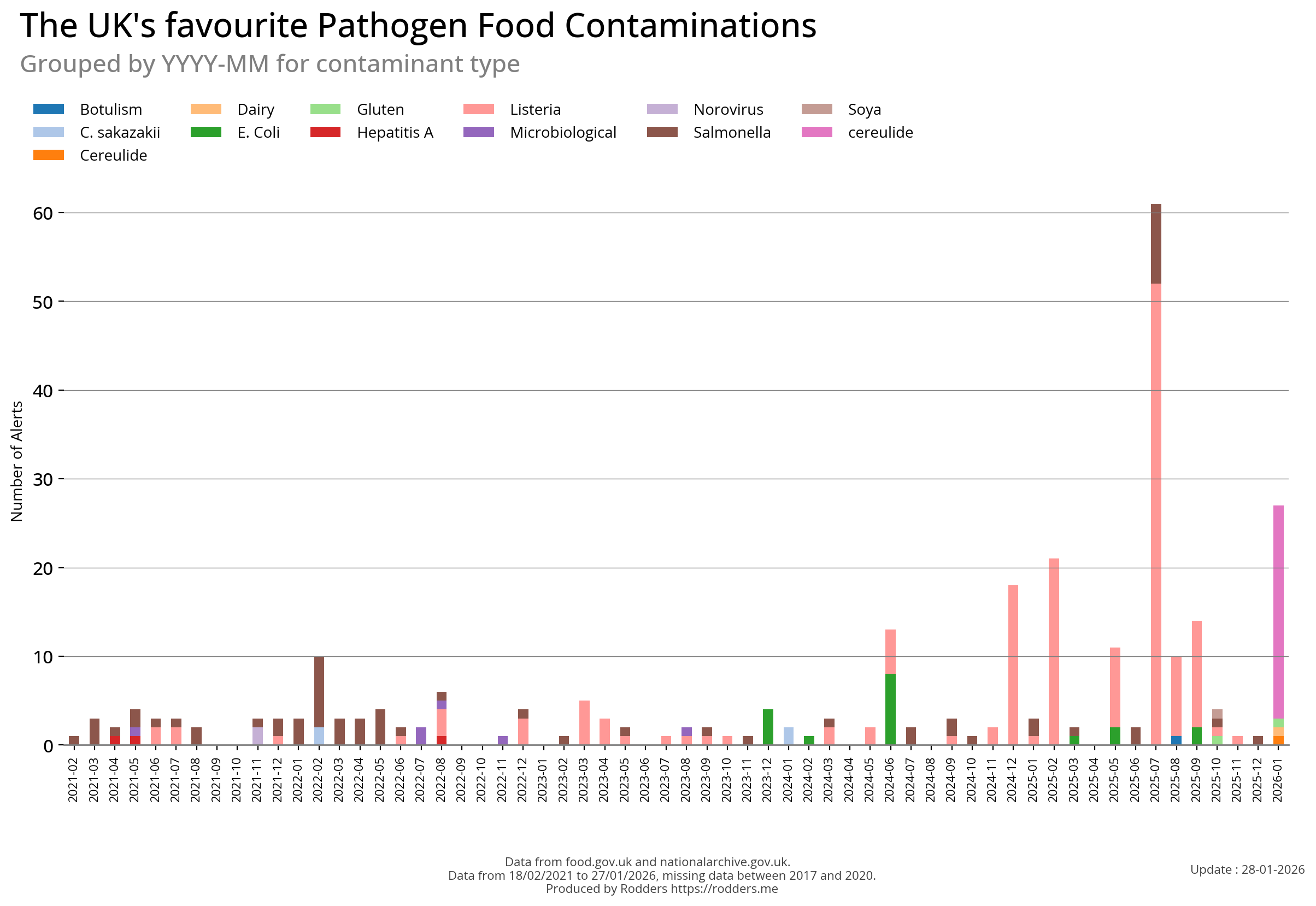
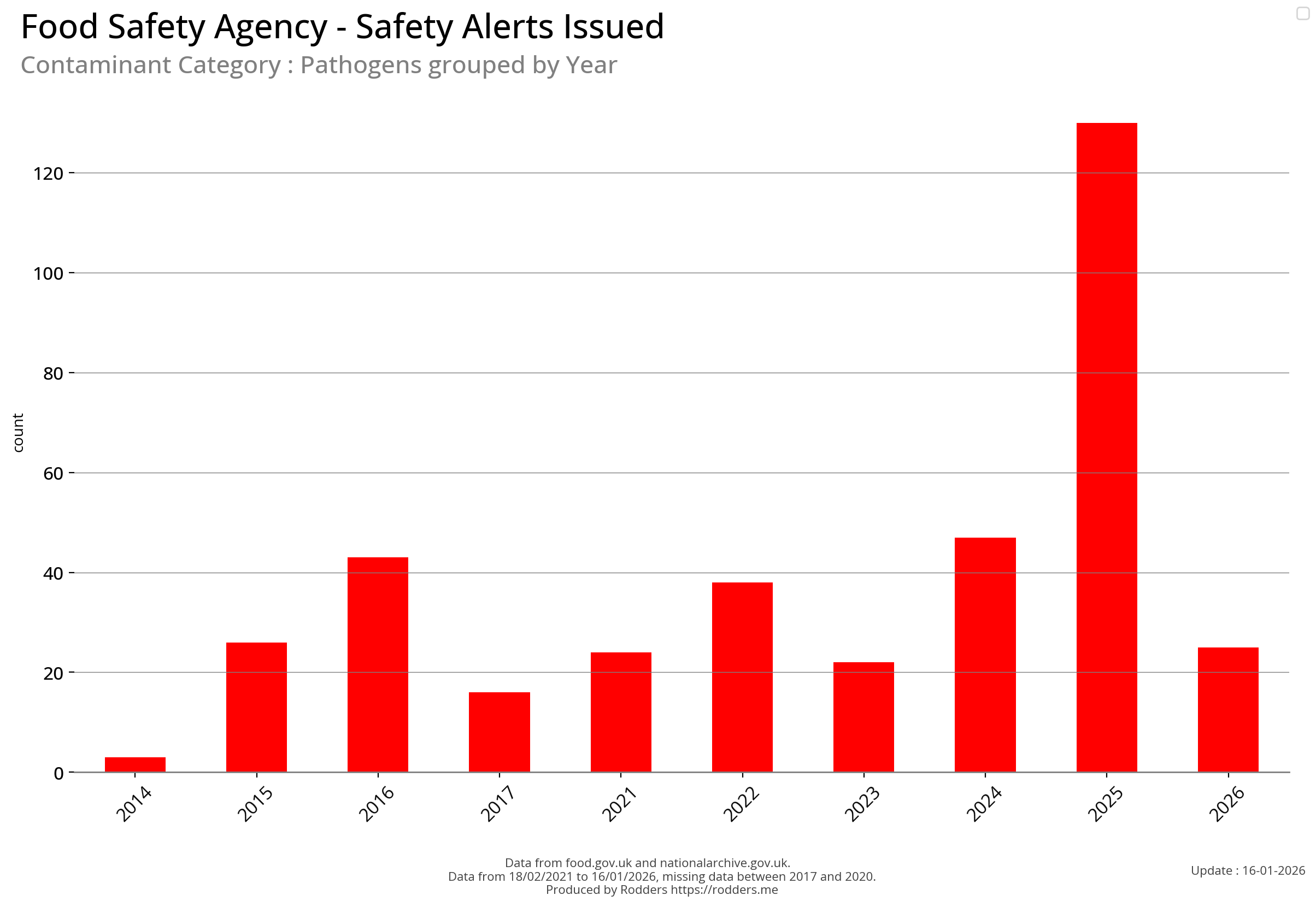
Pathogen Safety Alerts - Types by year
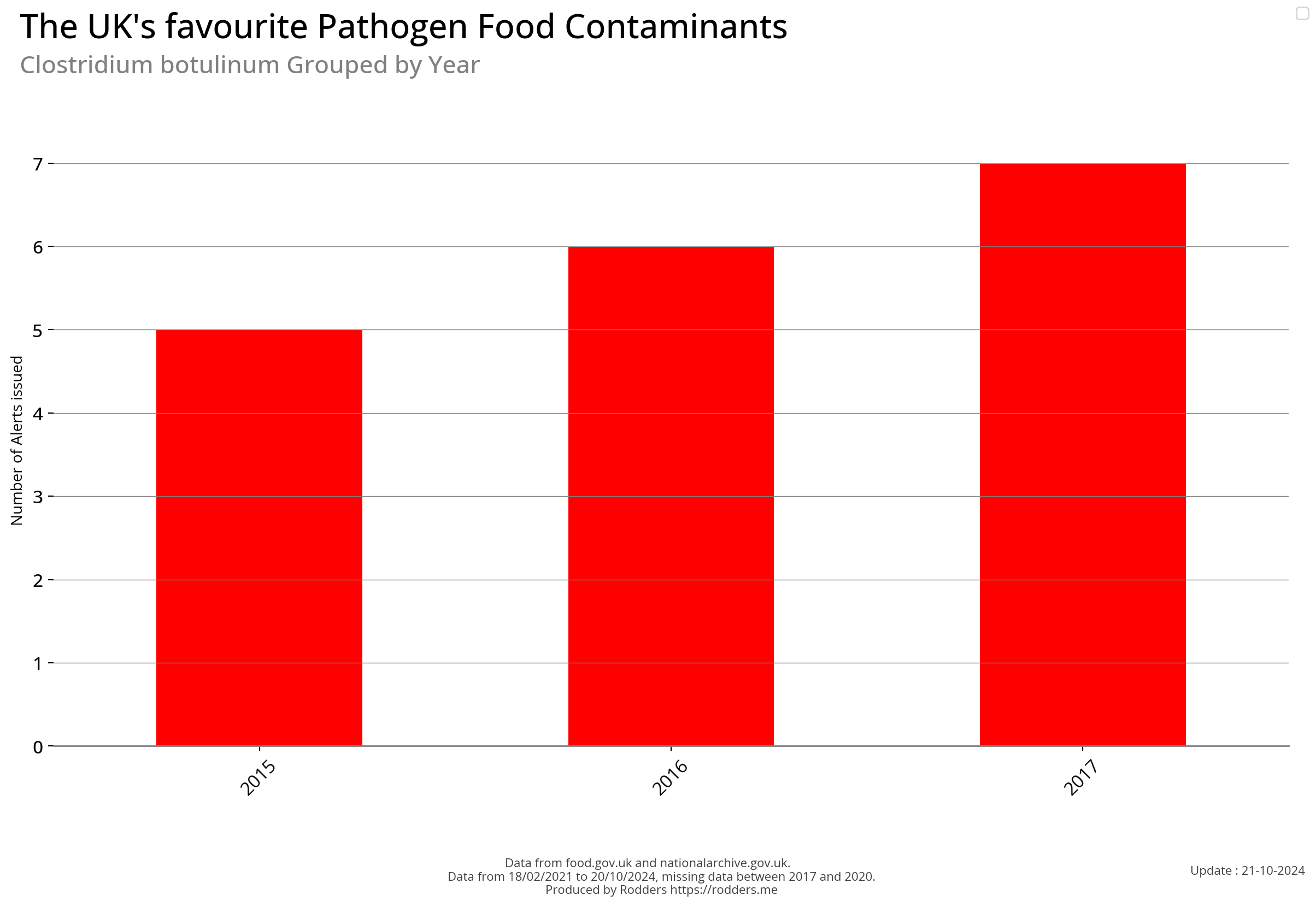
Note, data missing from 2017 to 2020.
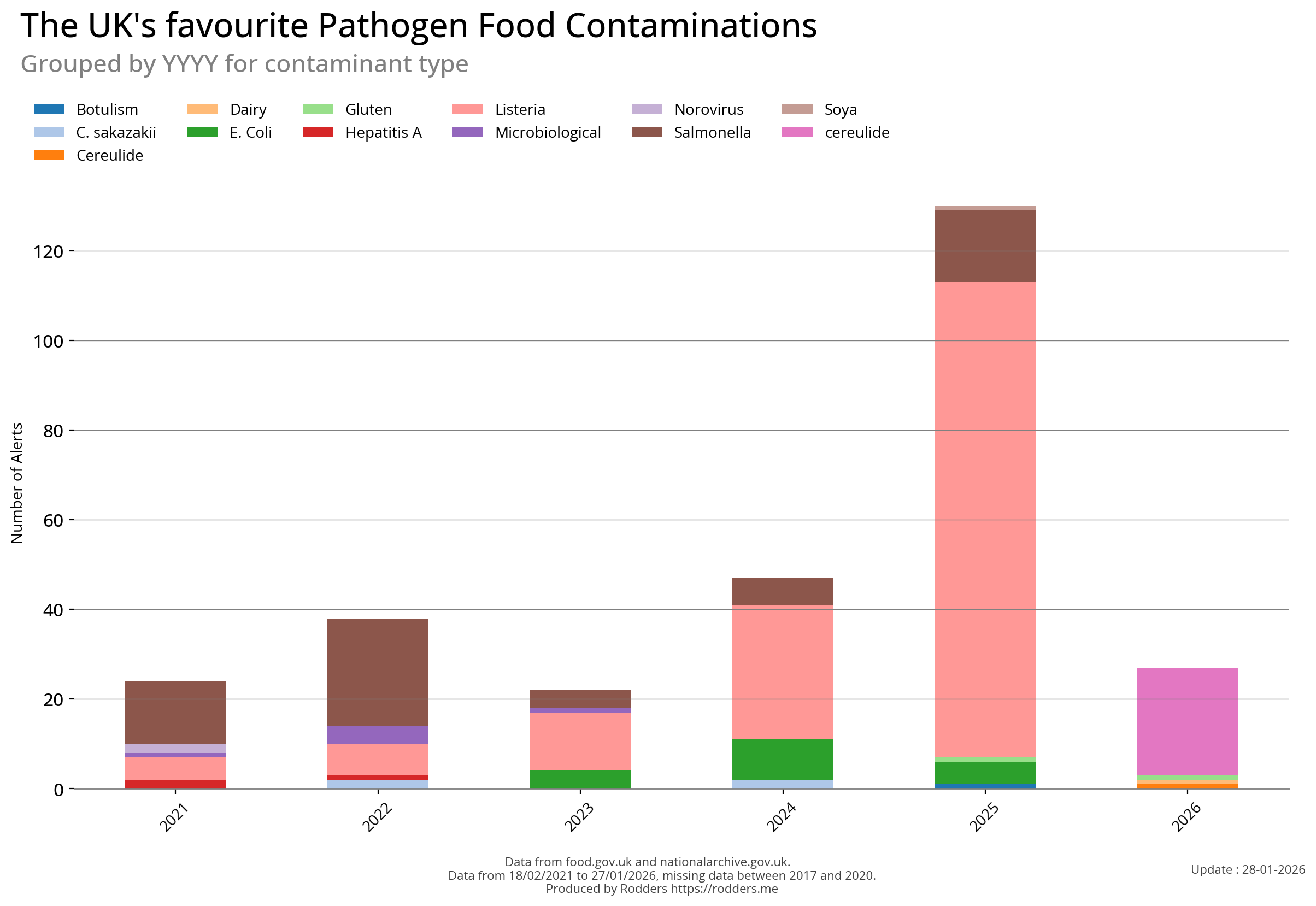
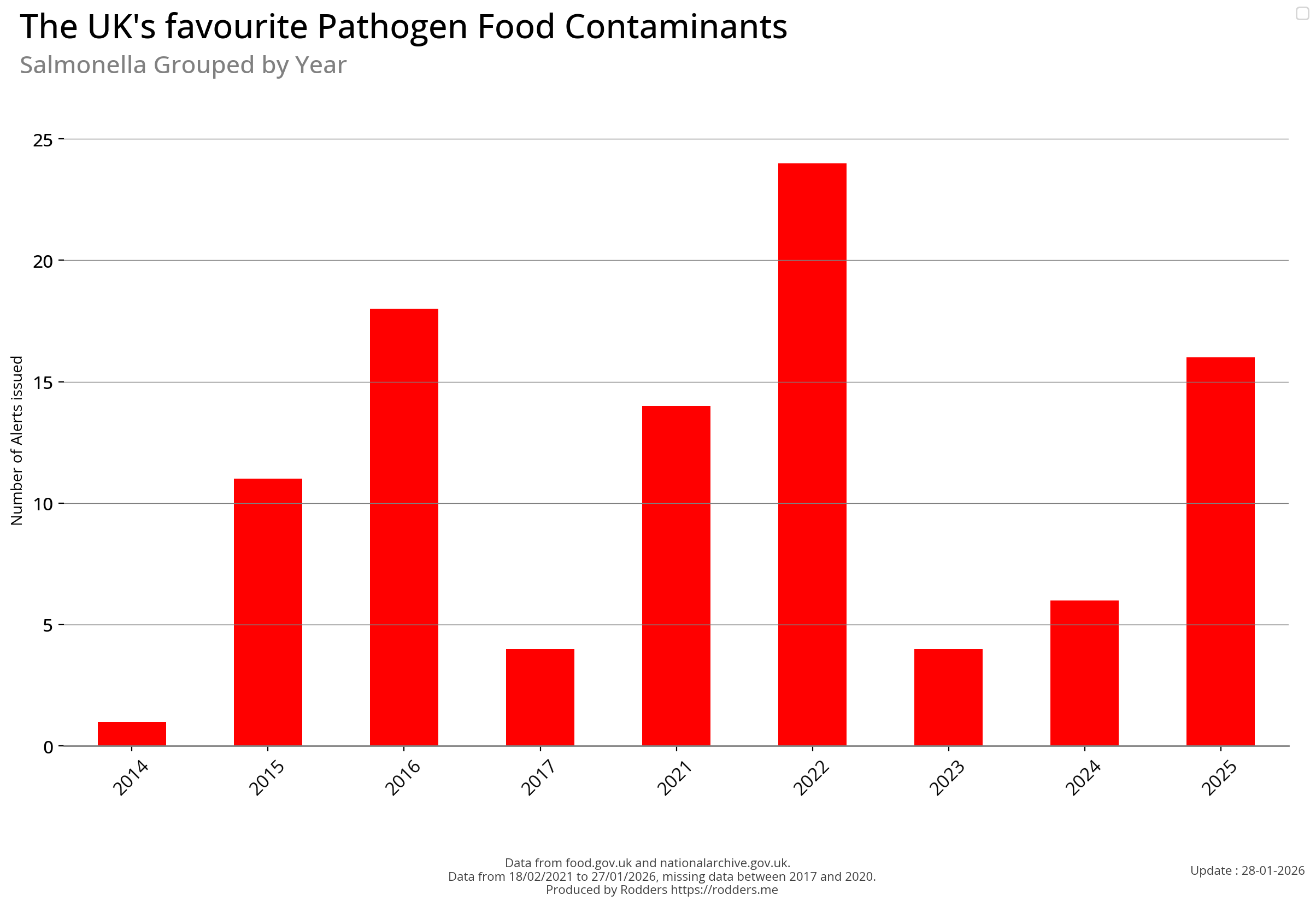
| Pathogen | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Listeria | 0 | 7 | 14 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 13 | 30 | 106 | 0 | 185 |
| Salmonella | 1 | 11 | 18 | 4 | 14 | 24 | 4 | 6 | 16 | 0 | 98 |
| cereulide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 24 |
| E. Coli | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 0 | 23 |
| Botulism | 0 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 18 |
| Microbiological | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| C. sakazakii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Hepatitis A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Norovirus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Gluten | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Dairy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Clostridium botulinum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Food Poisoning | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Cereulide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Rhizopus oryzae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Campylobacter | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Soya | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Top
Time Series Cross-Sectional Visualisations of Pathogen Types
Top
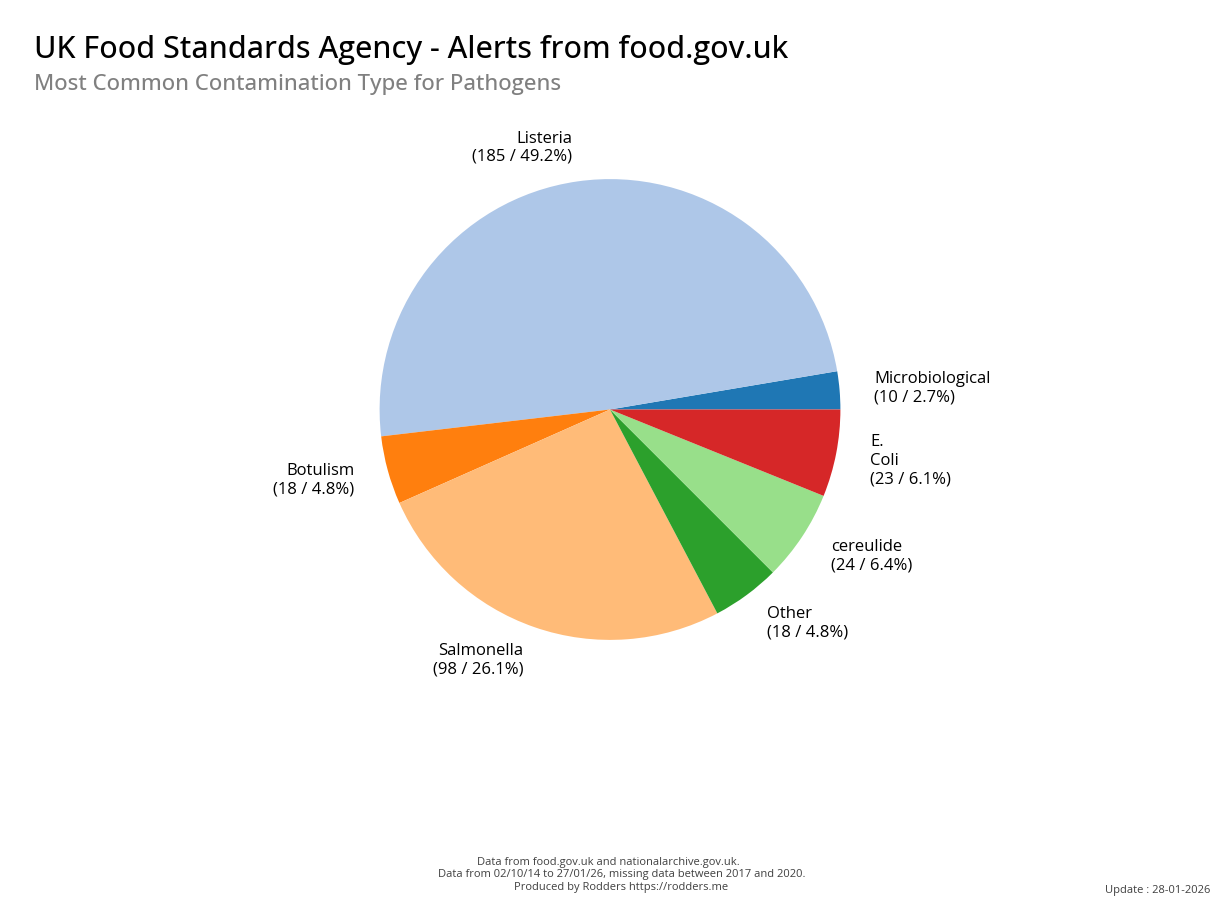
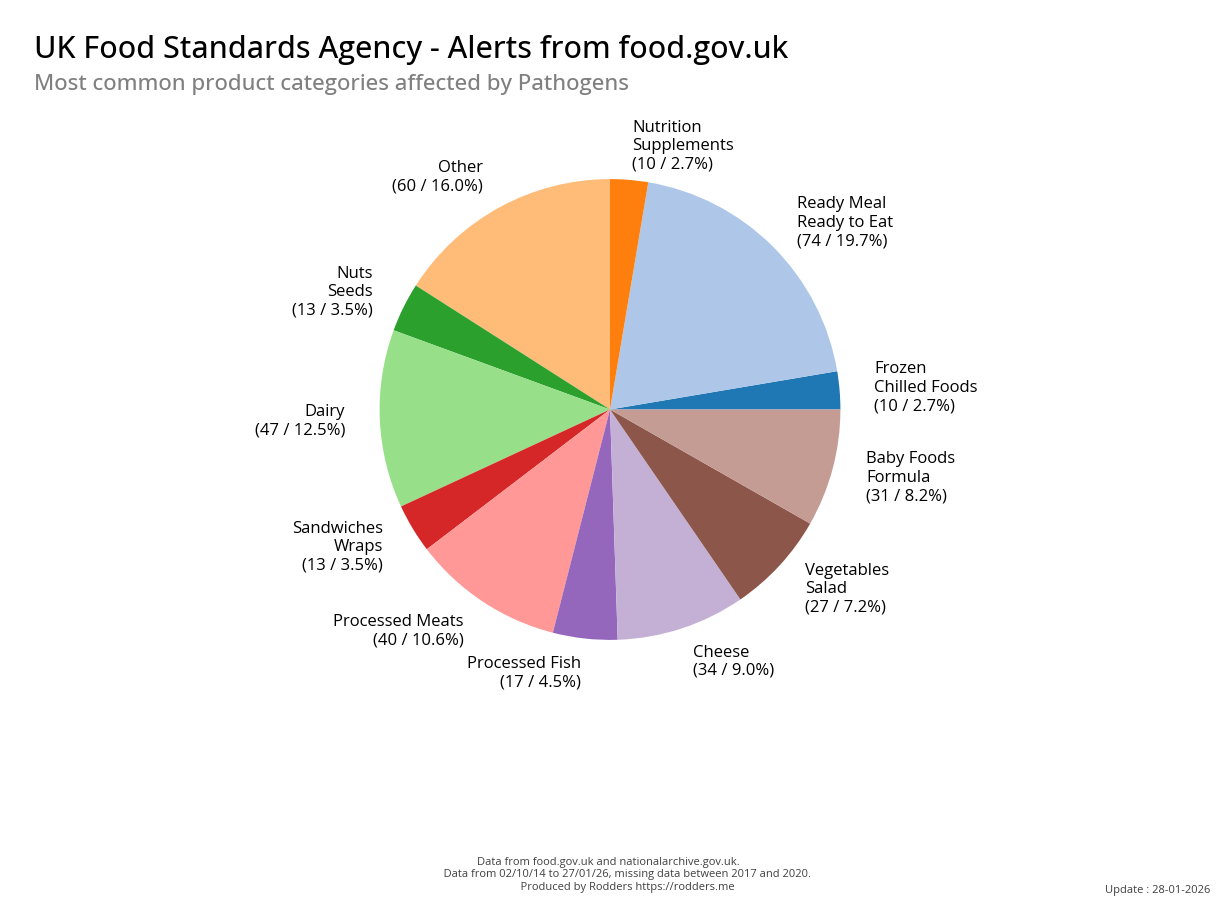
Safety Alert Distribution by Pathogen Types
Top
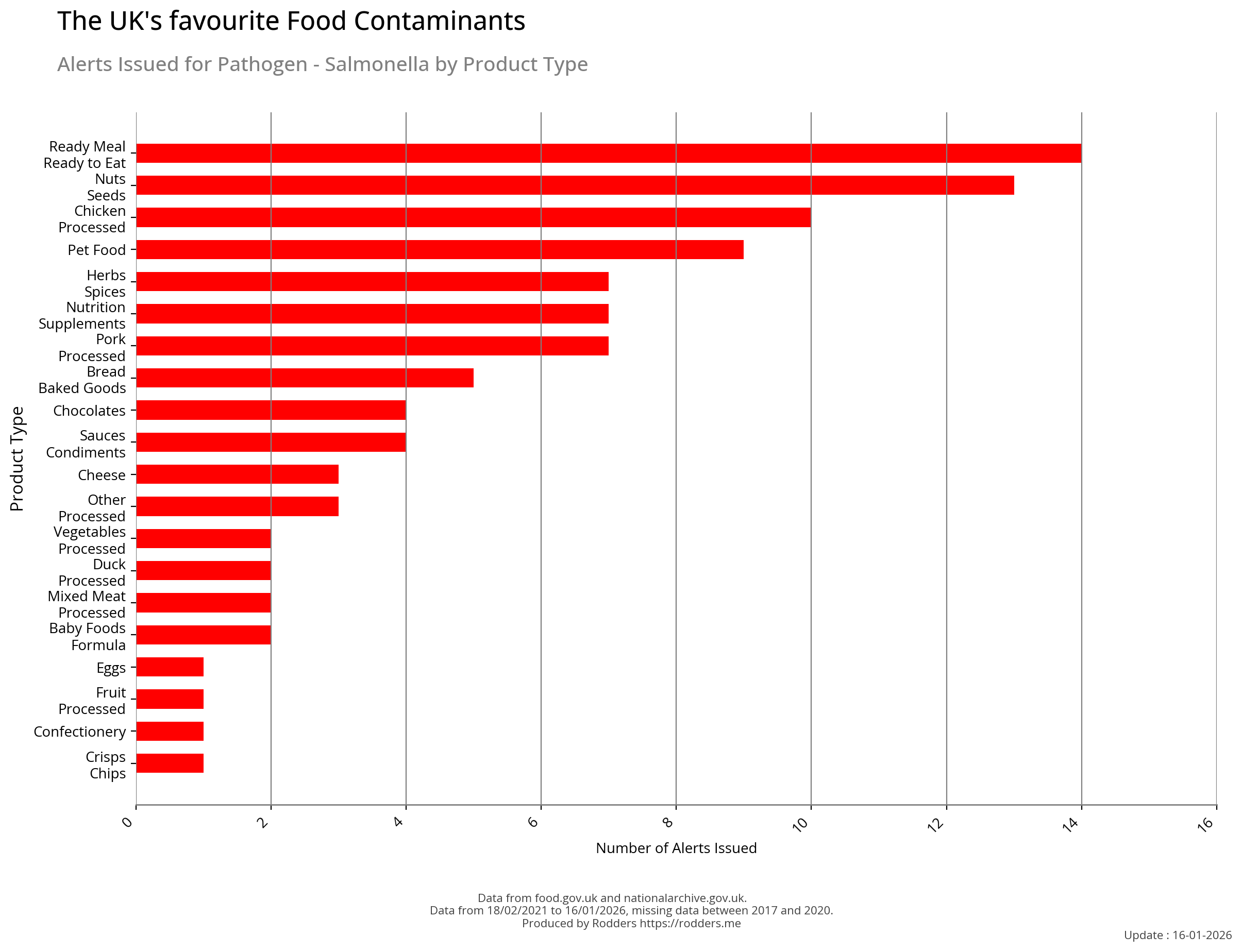
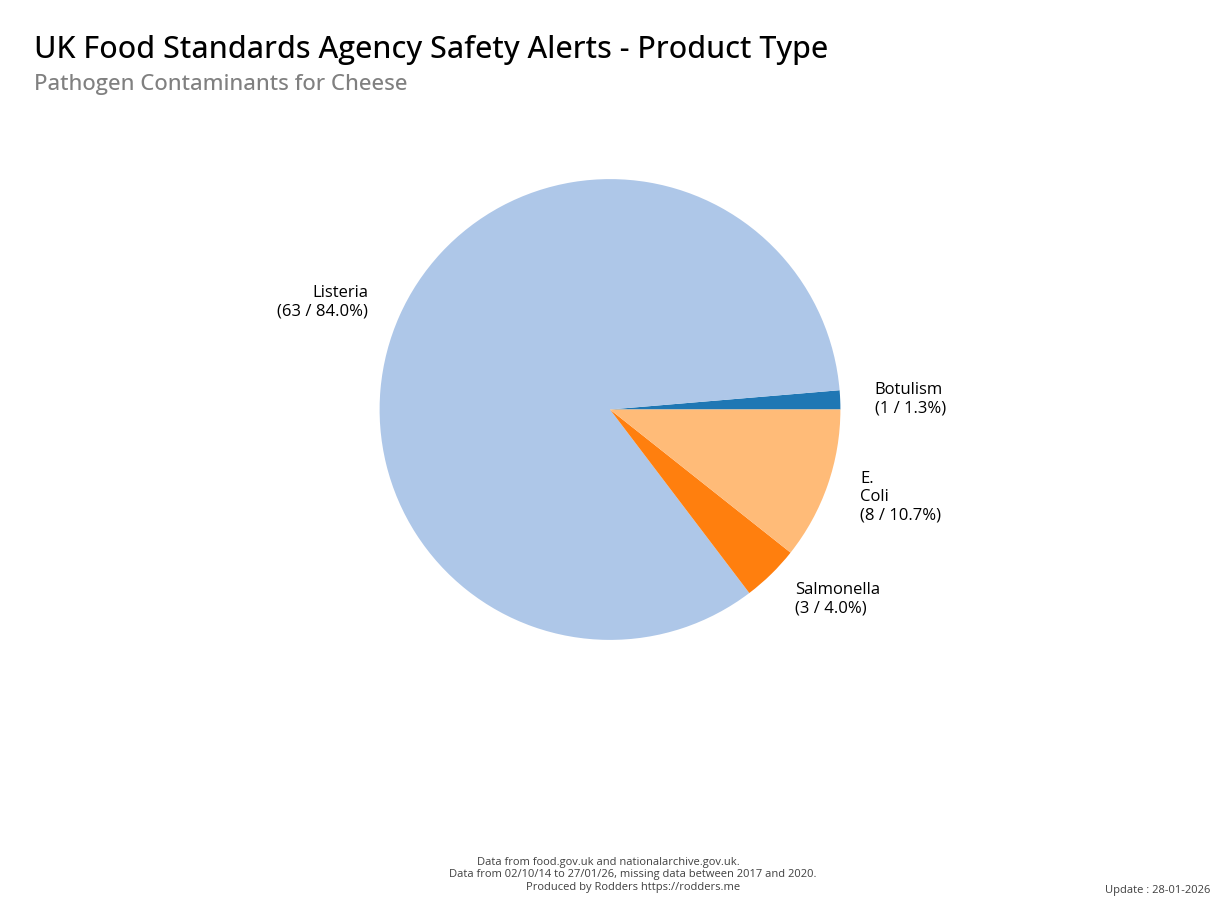
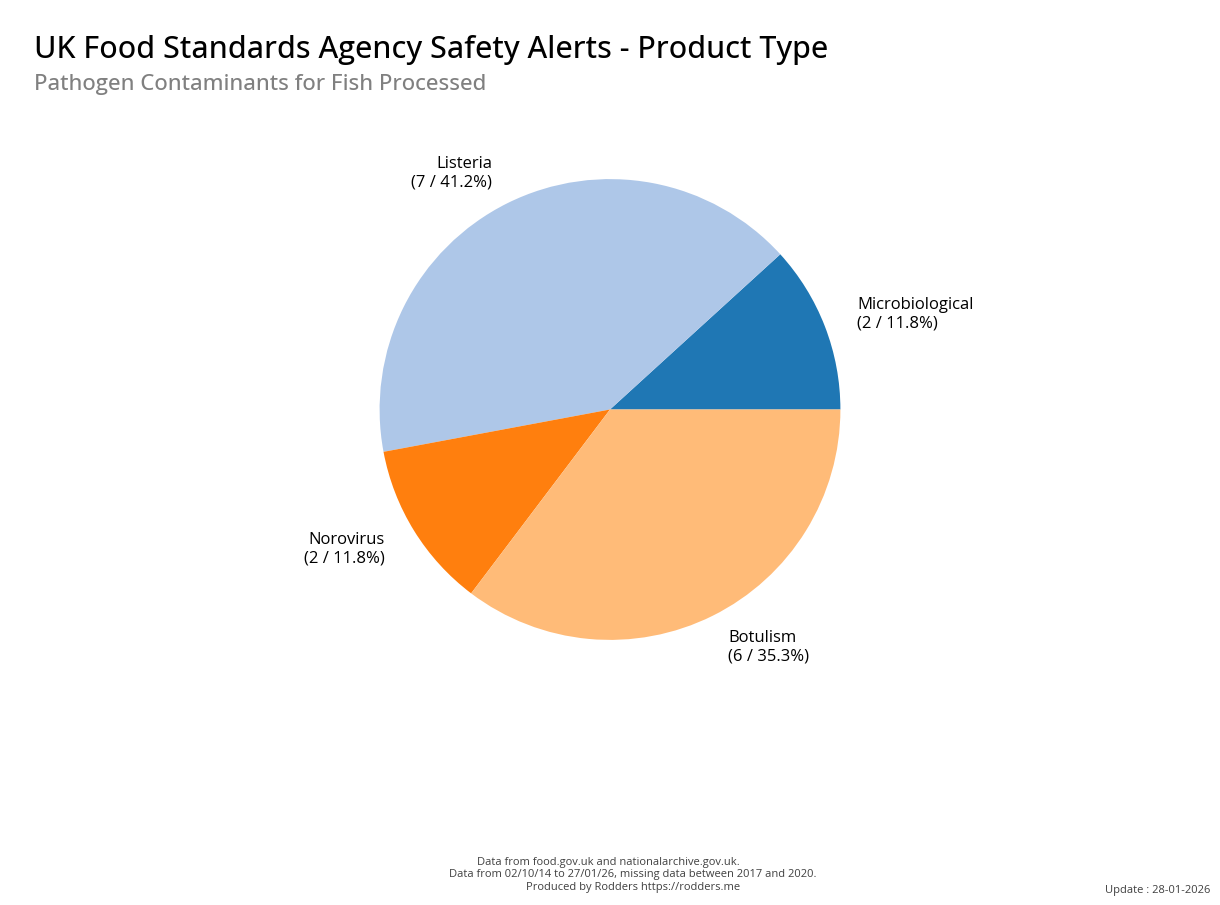
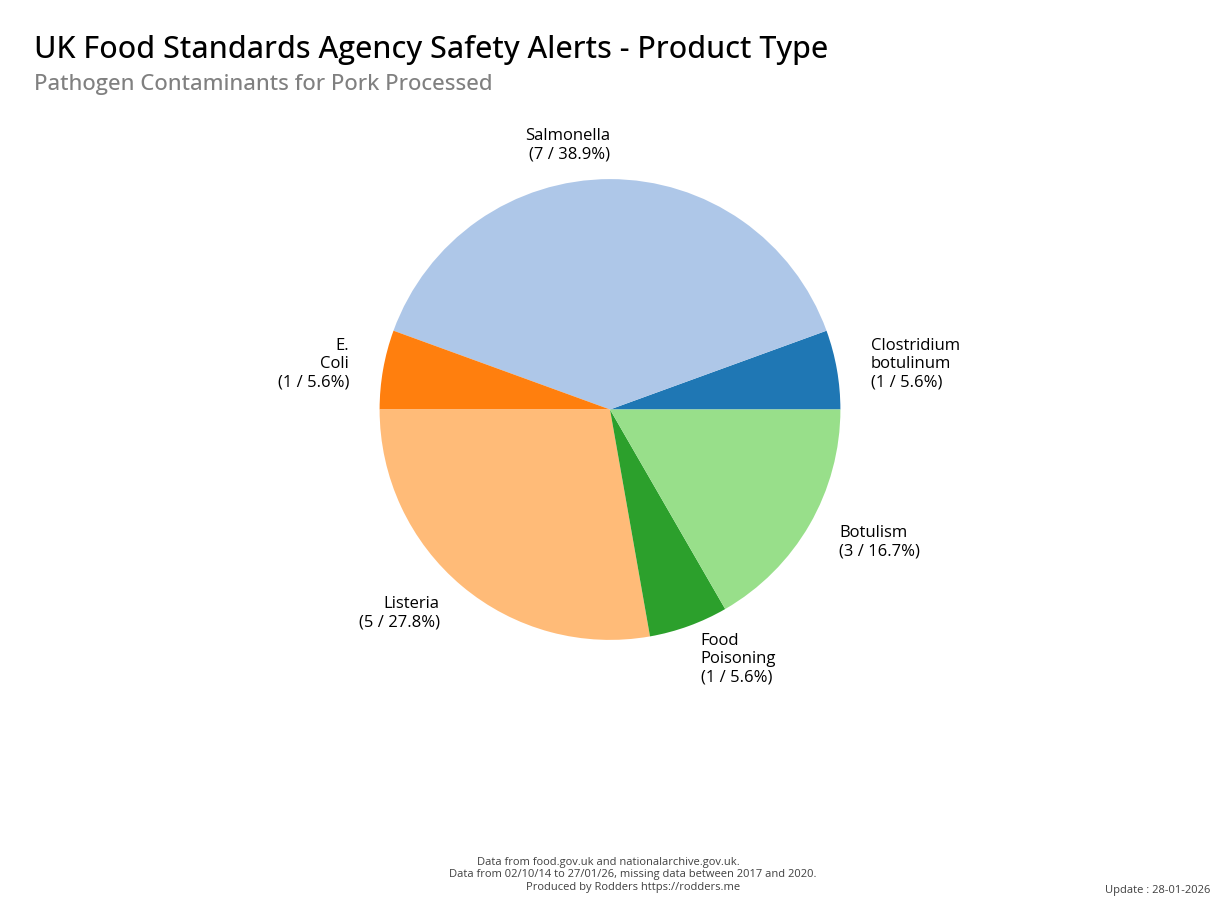
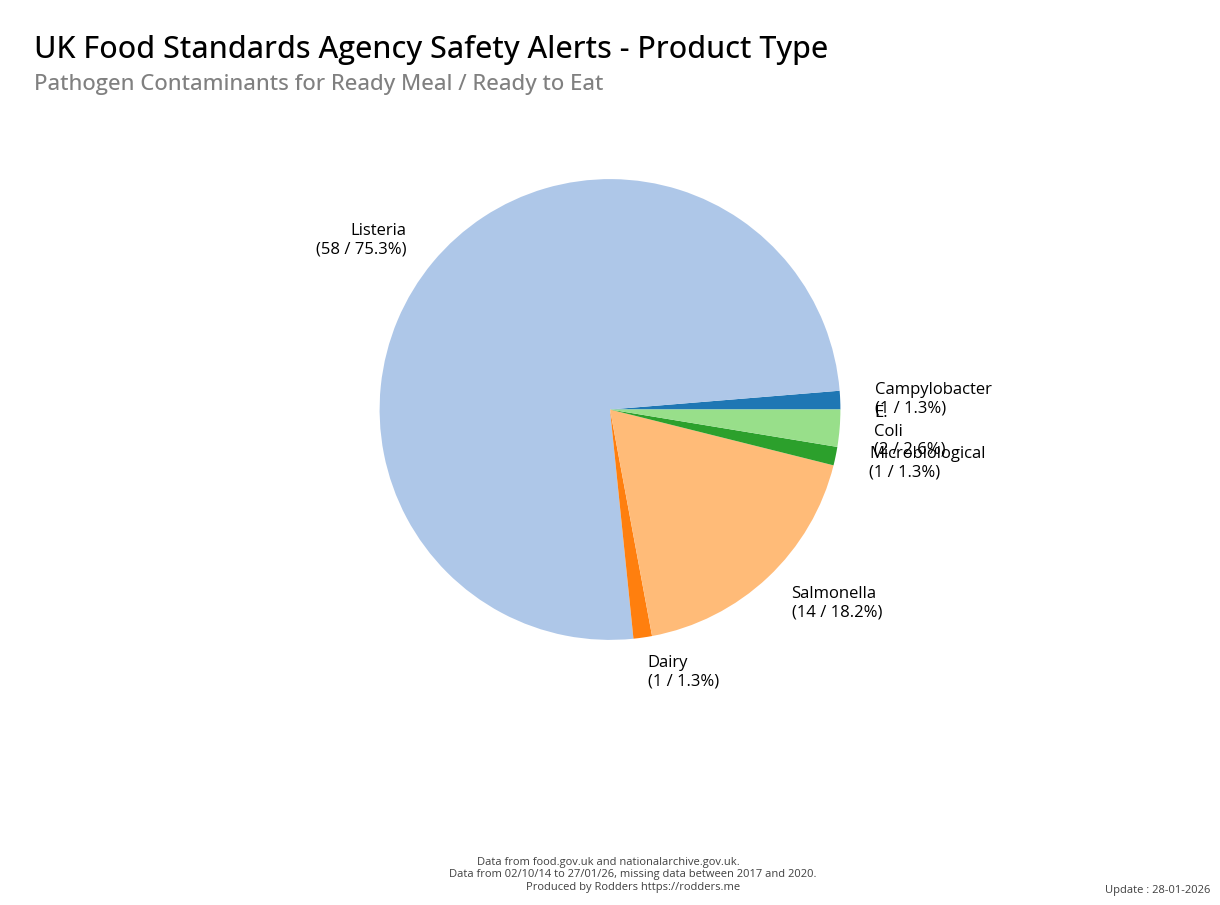
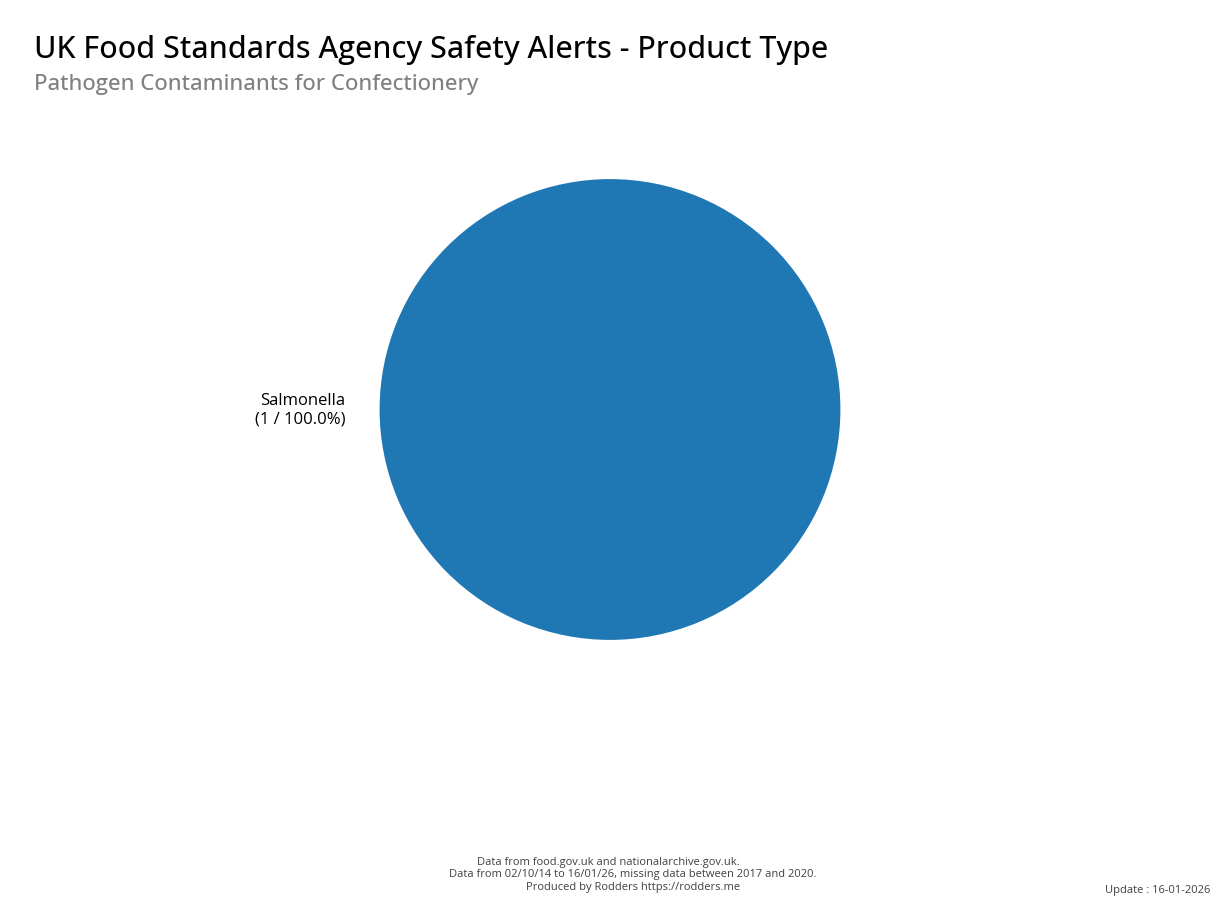
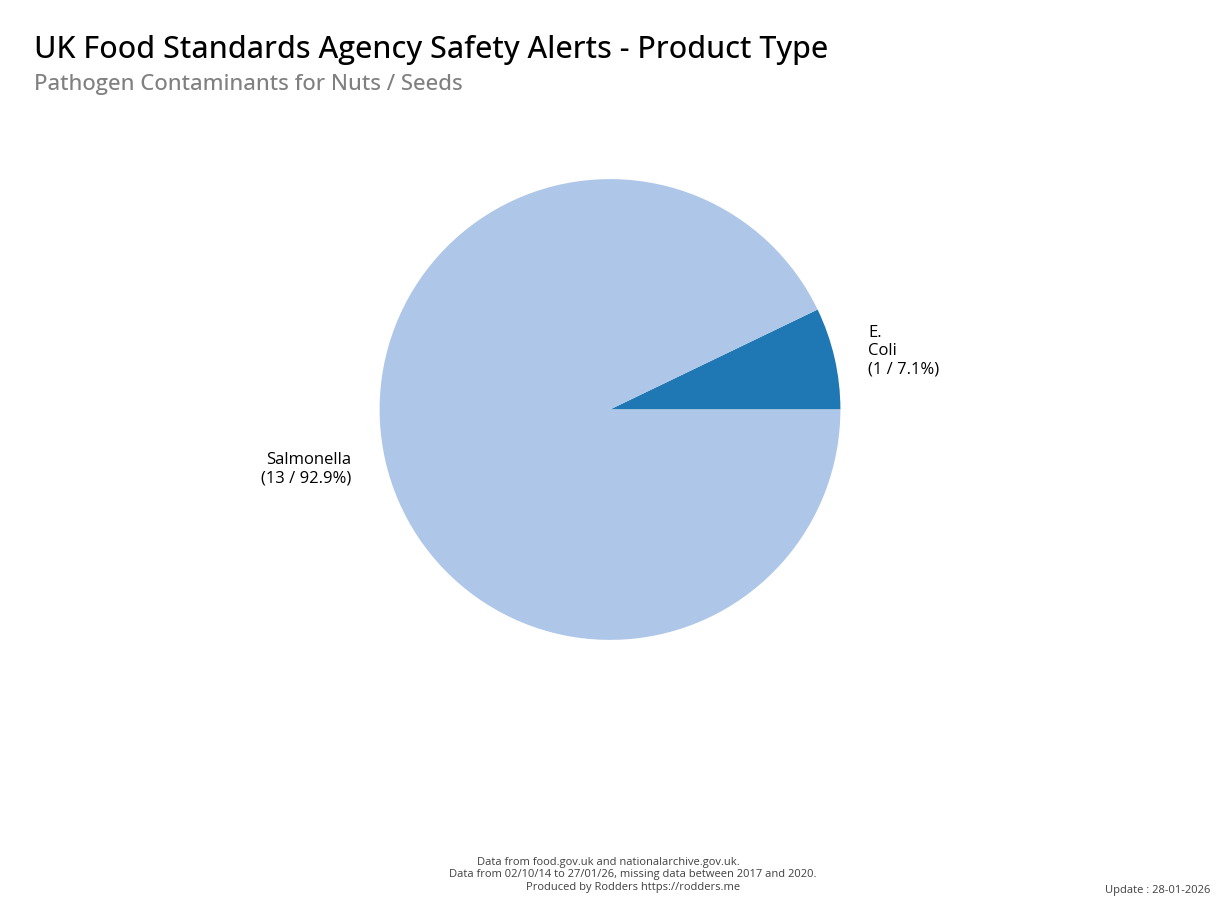
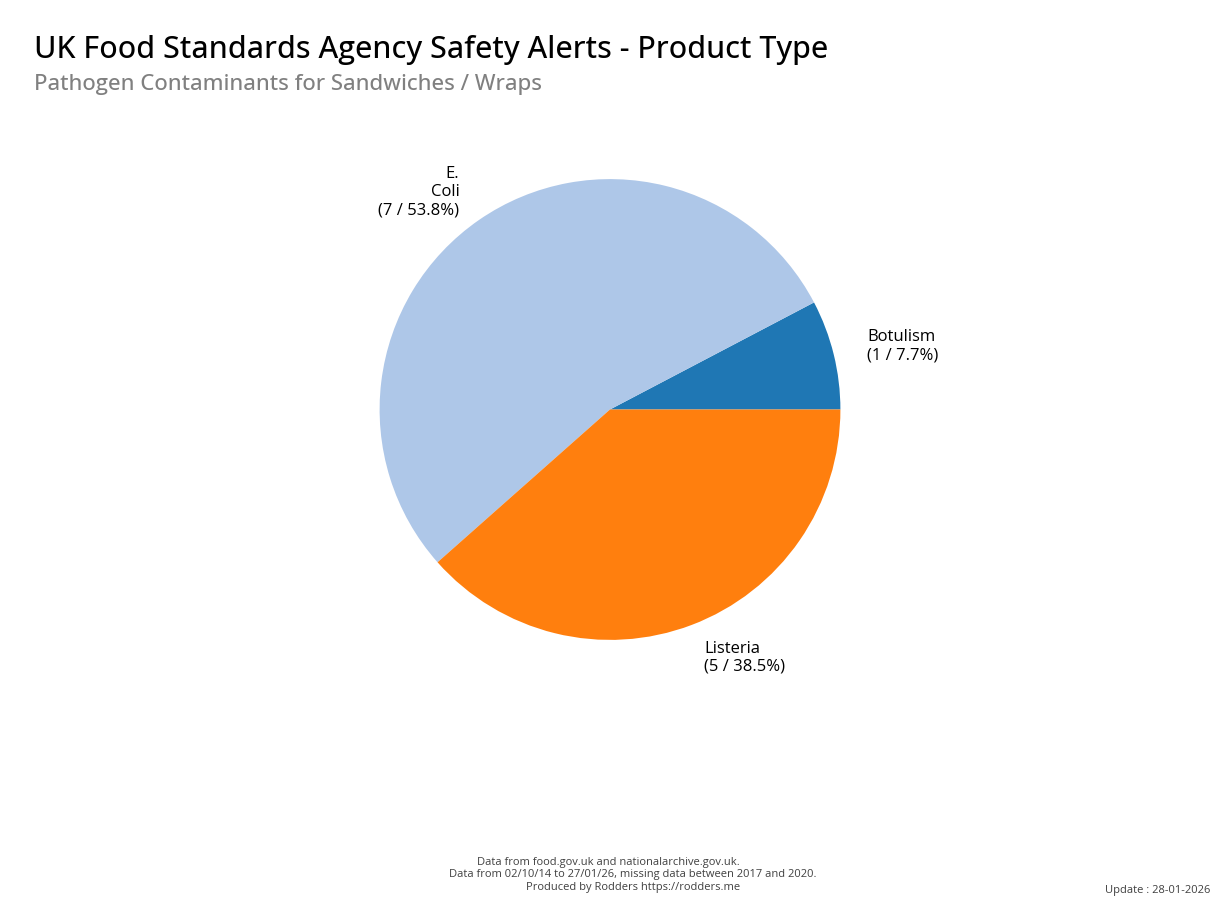
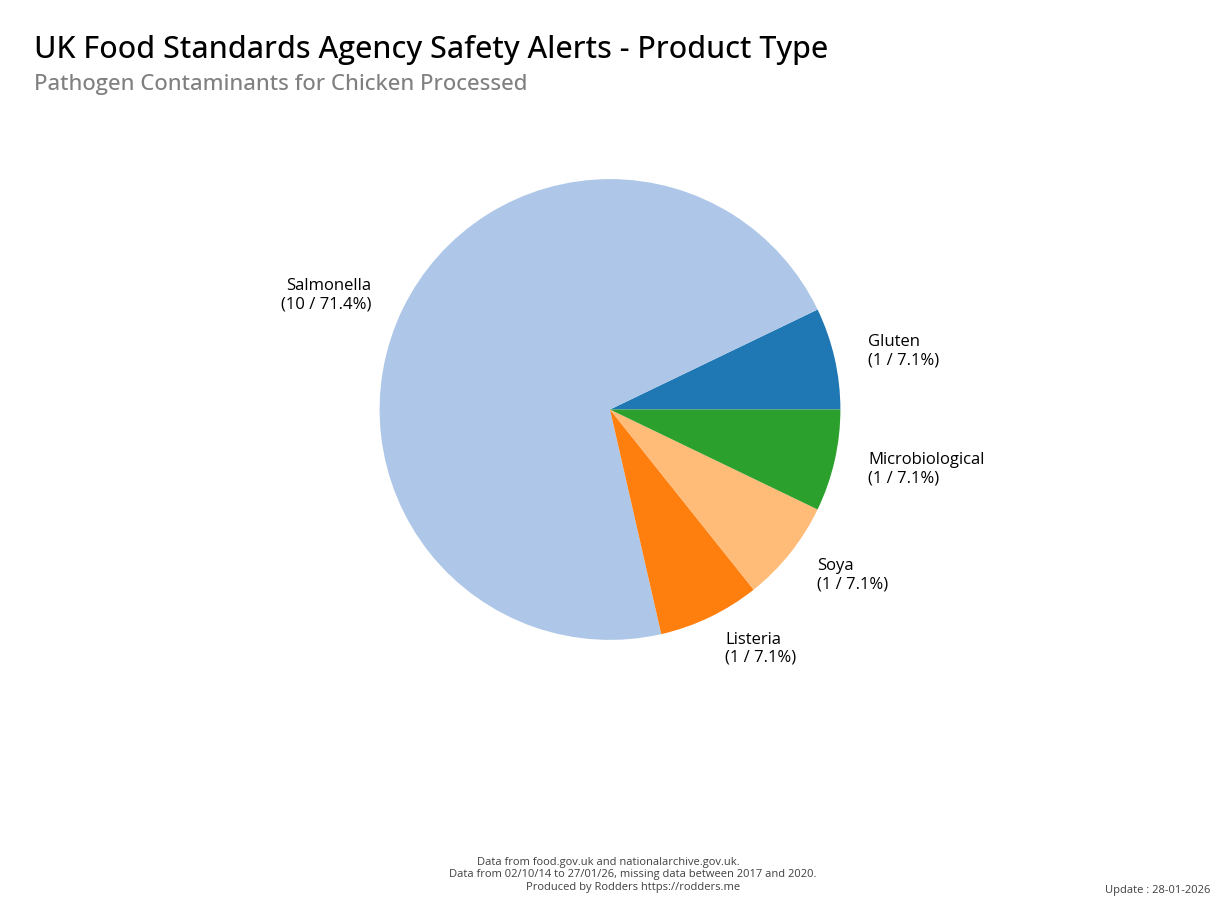
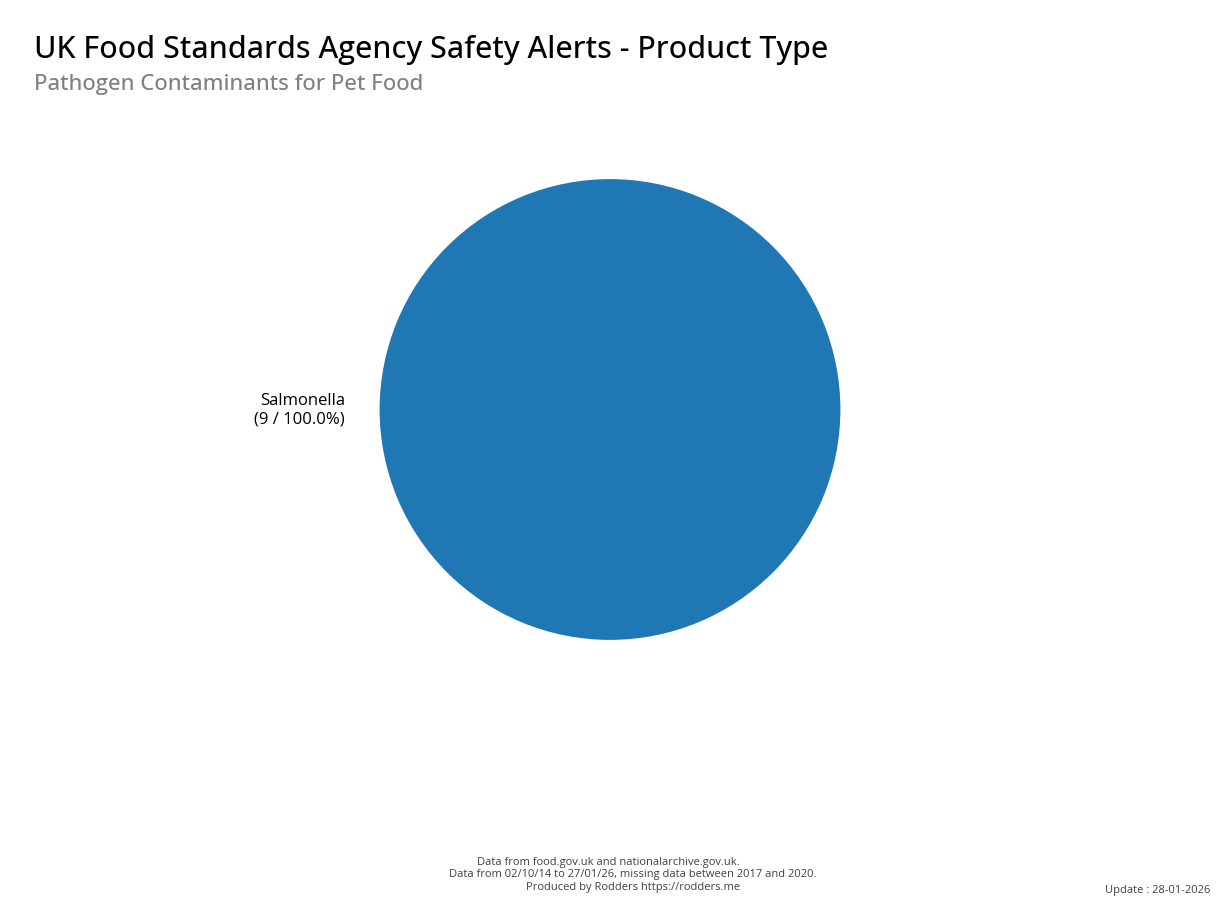
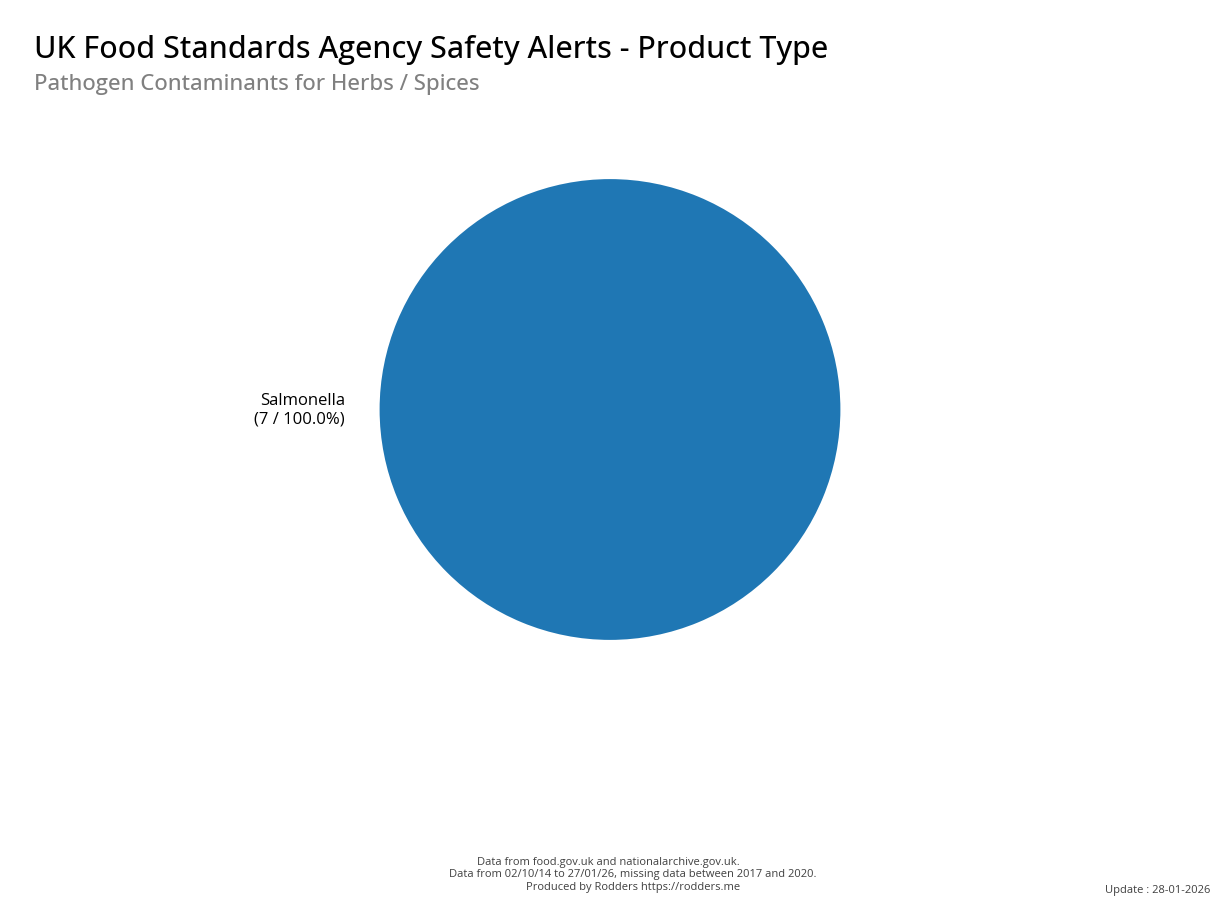
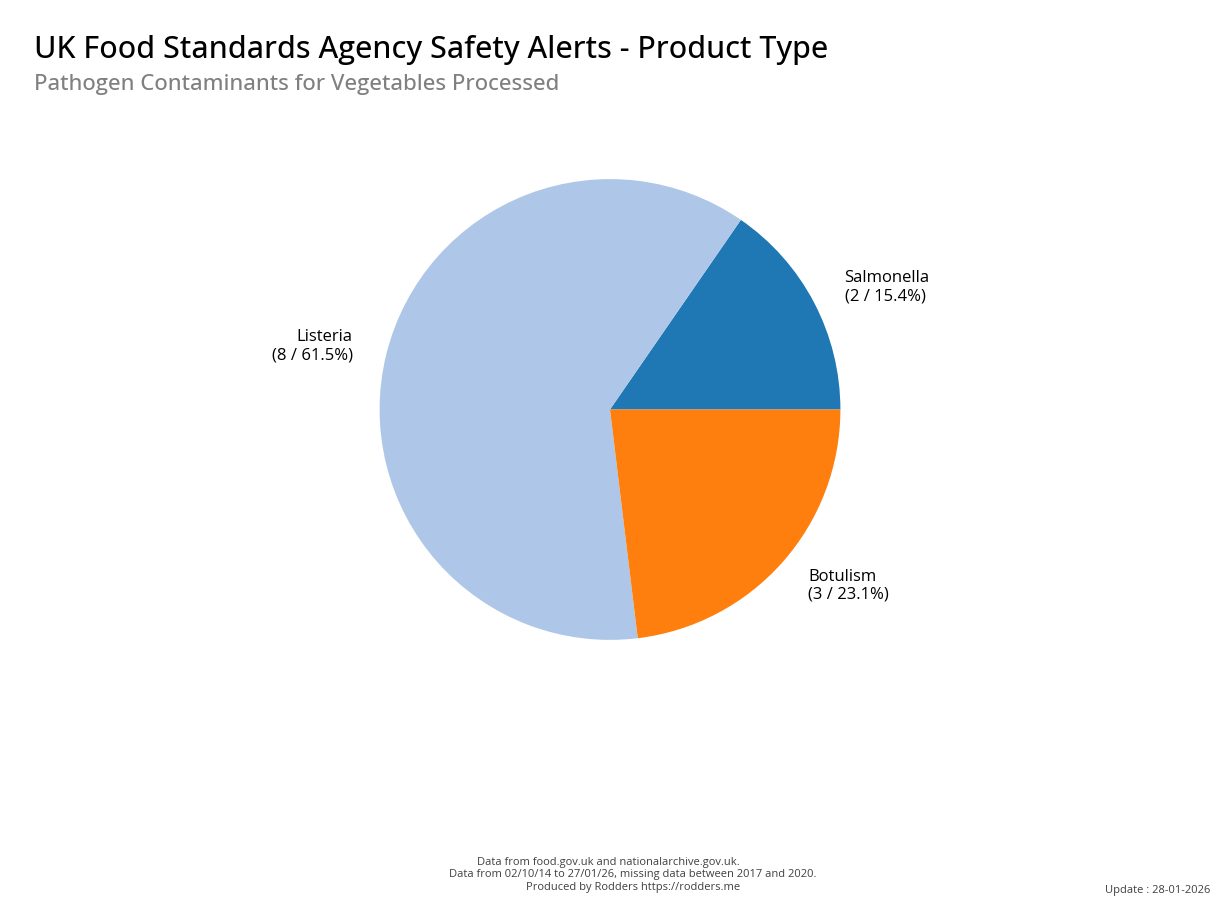
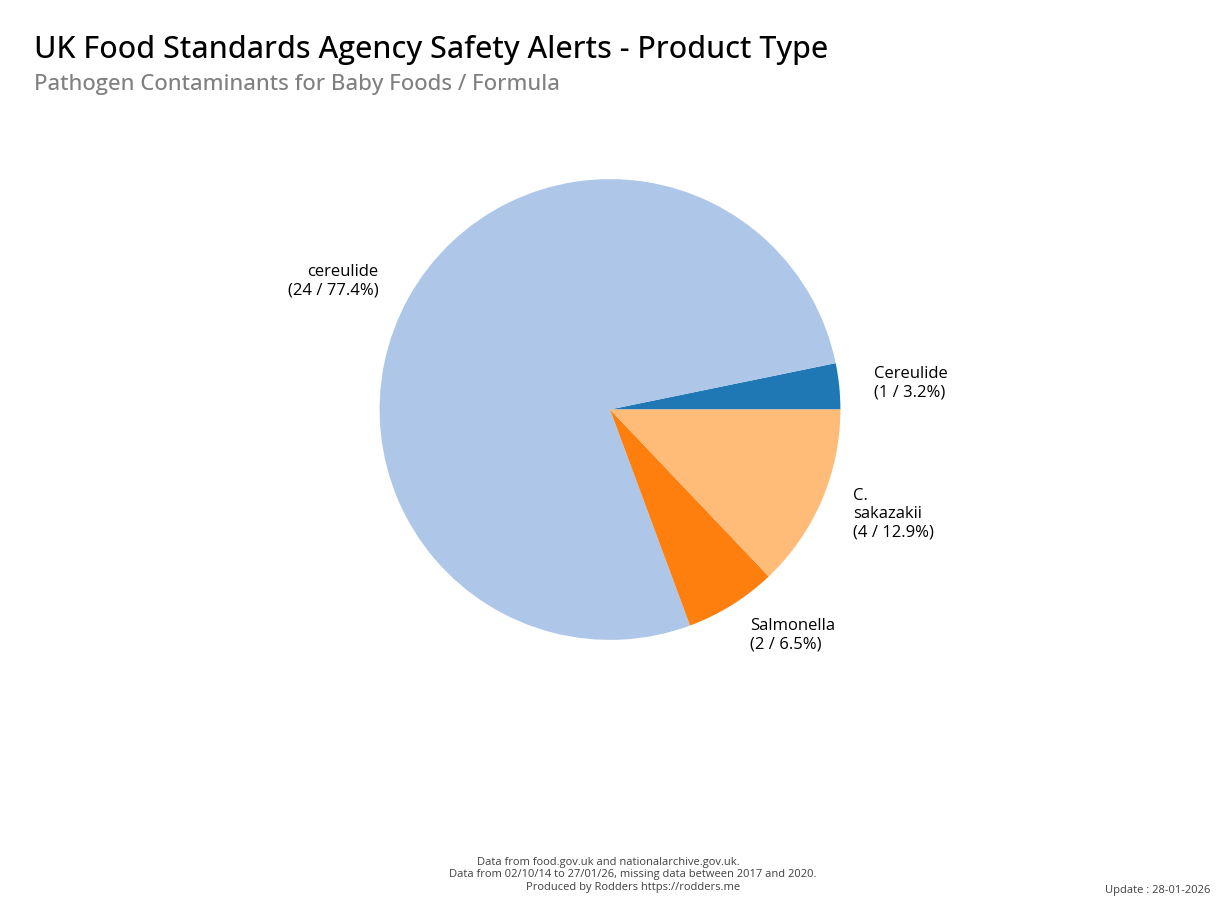
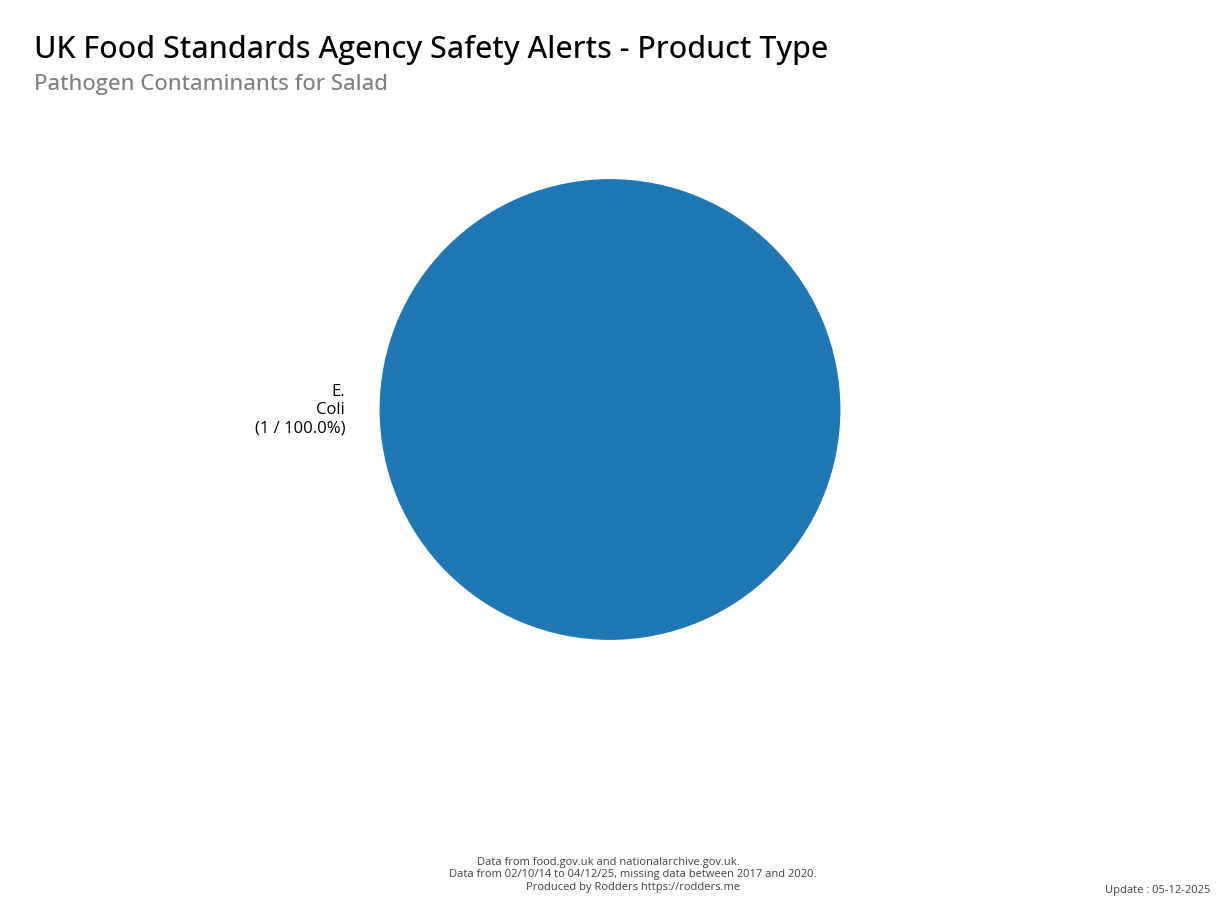
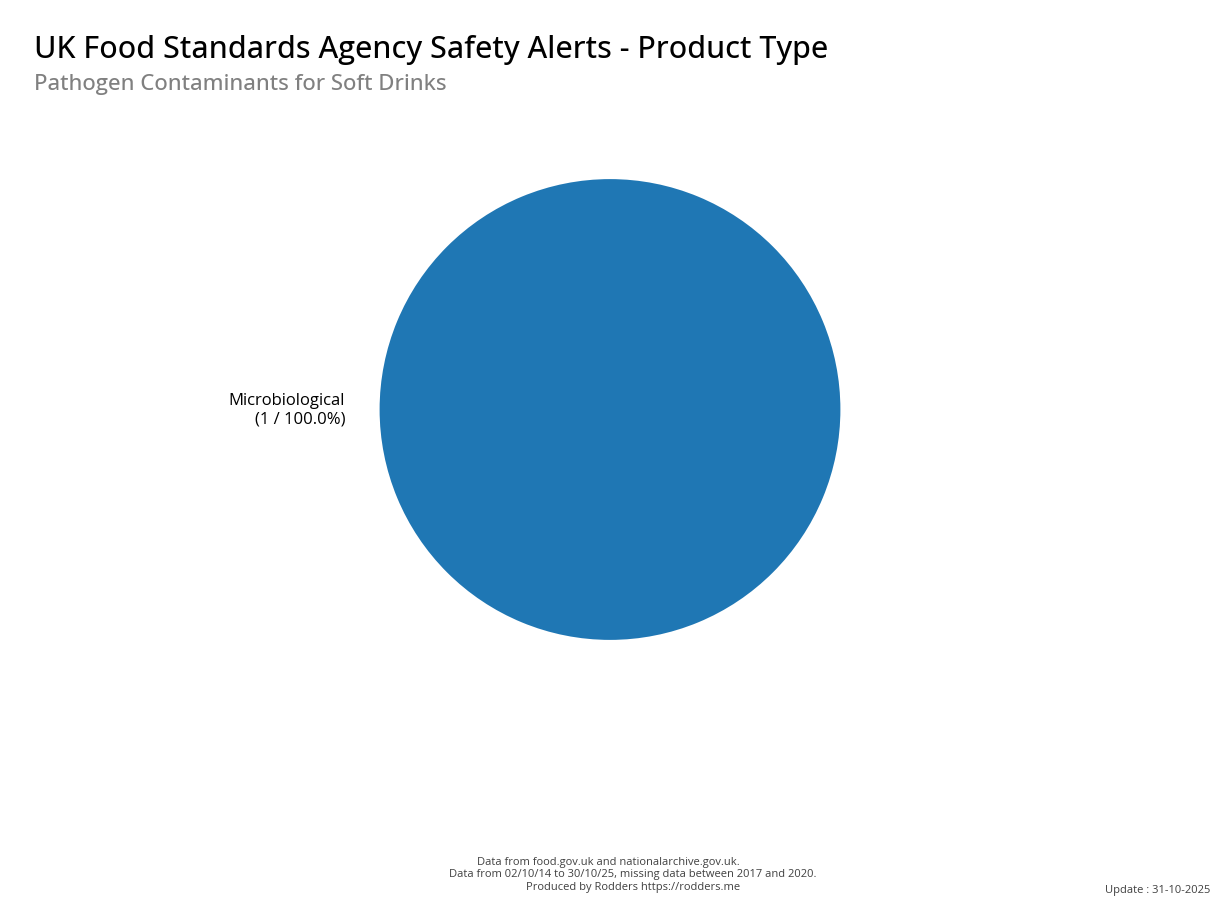
Safety Alert Distribution by Product Types
Top
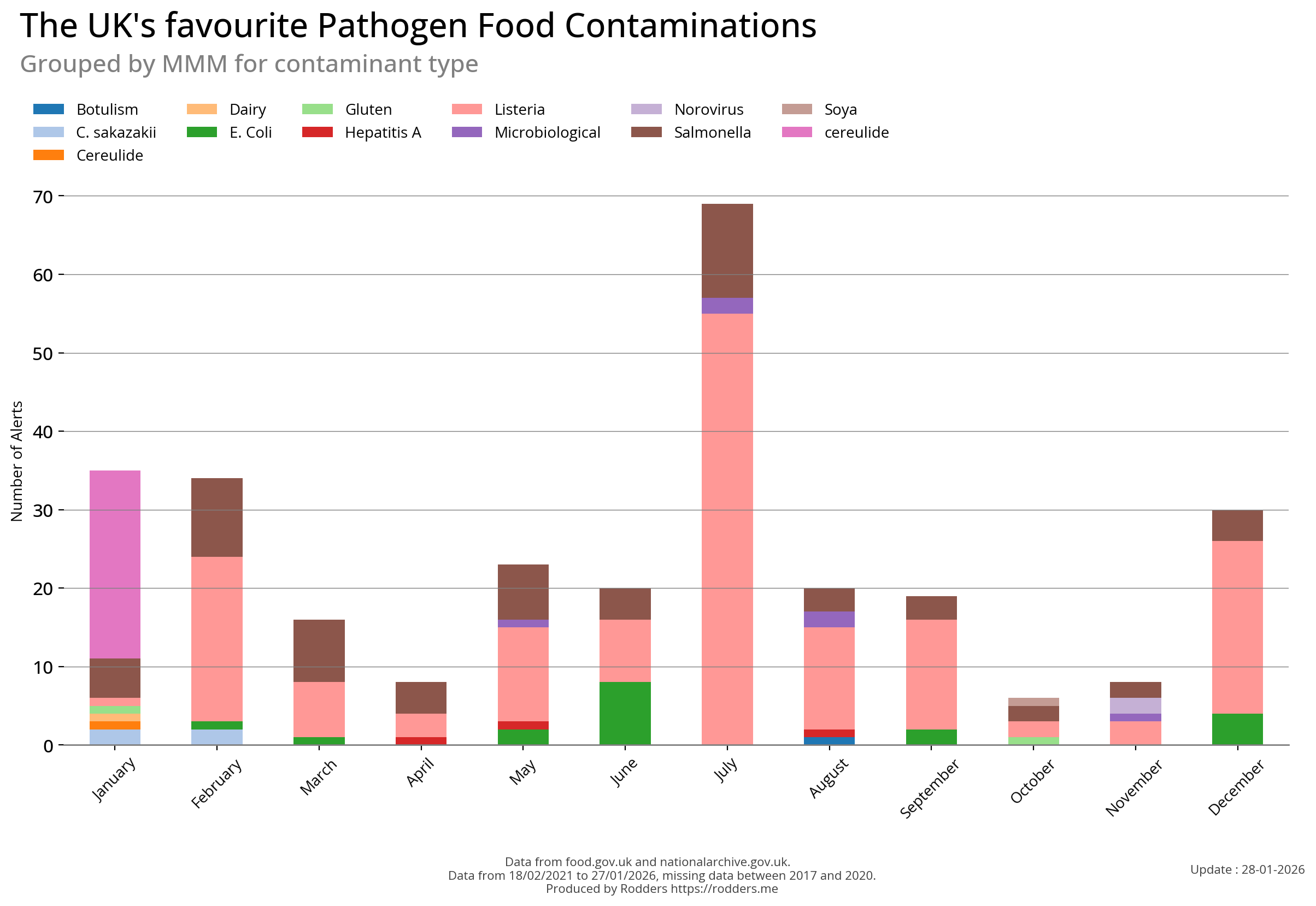
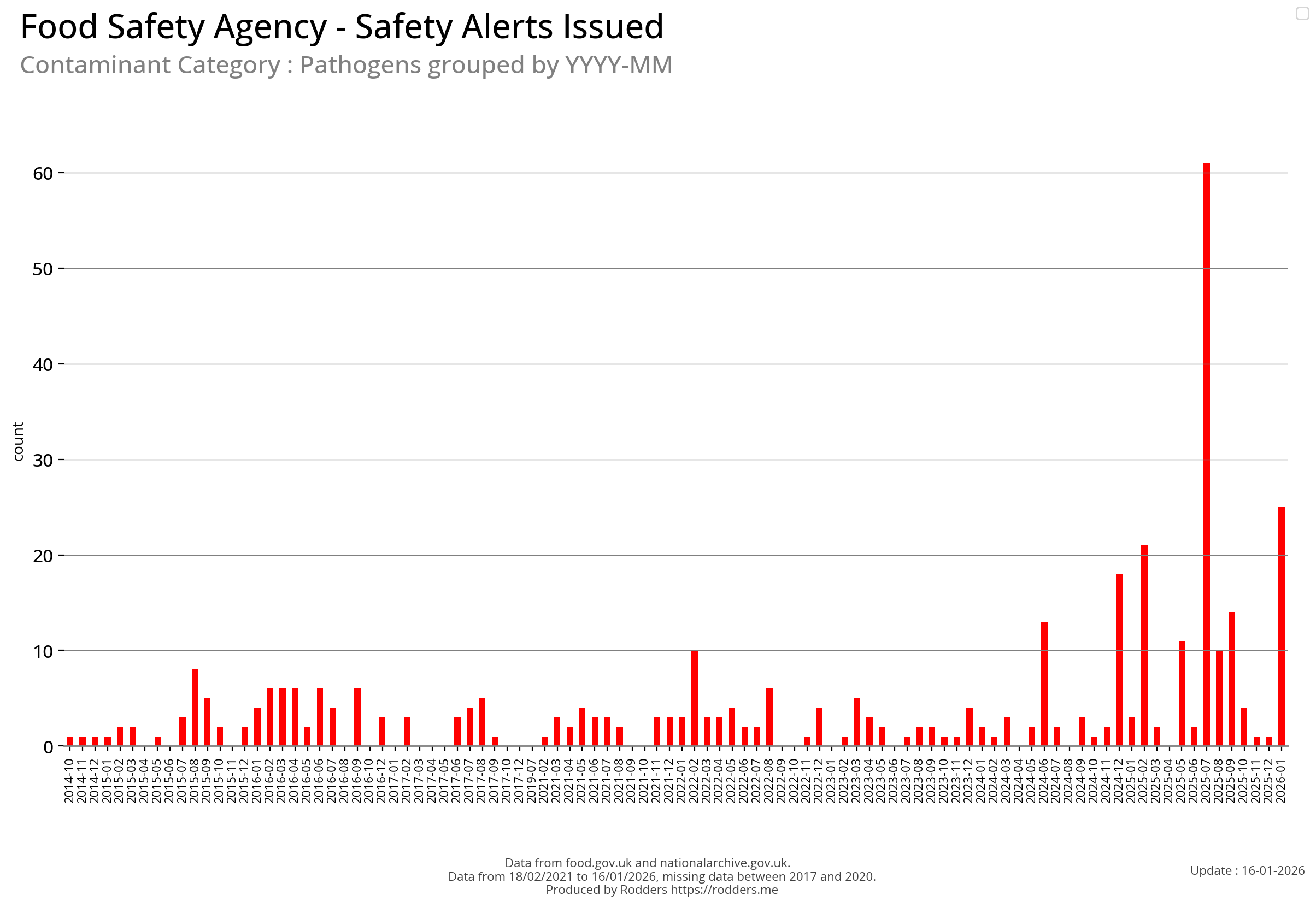
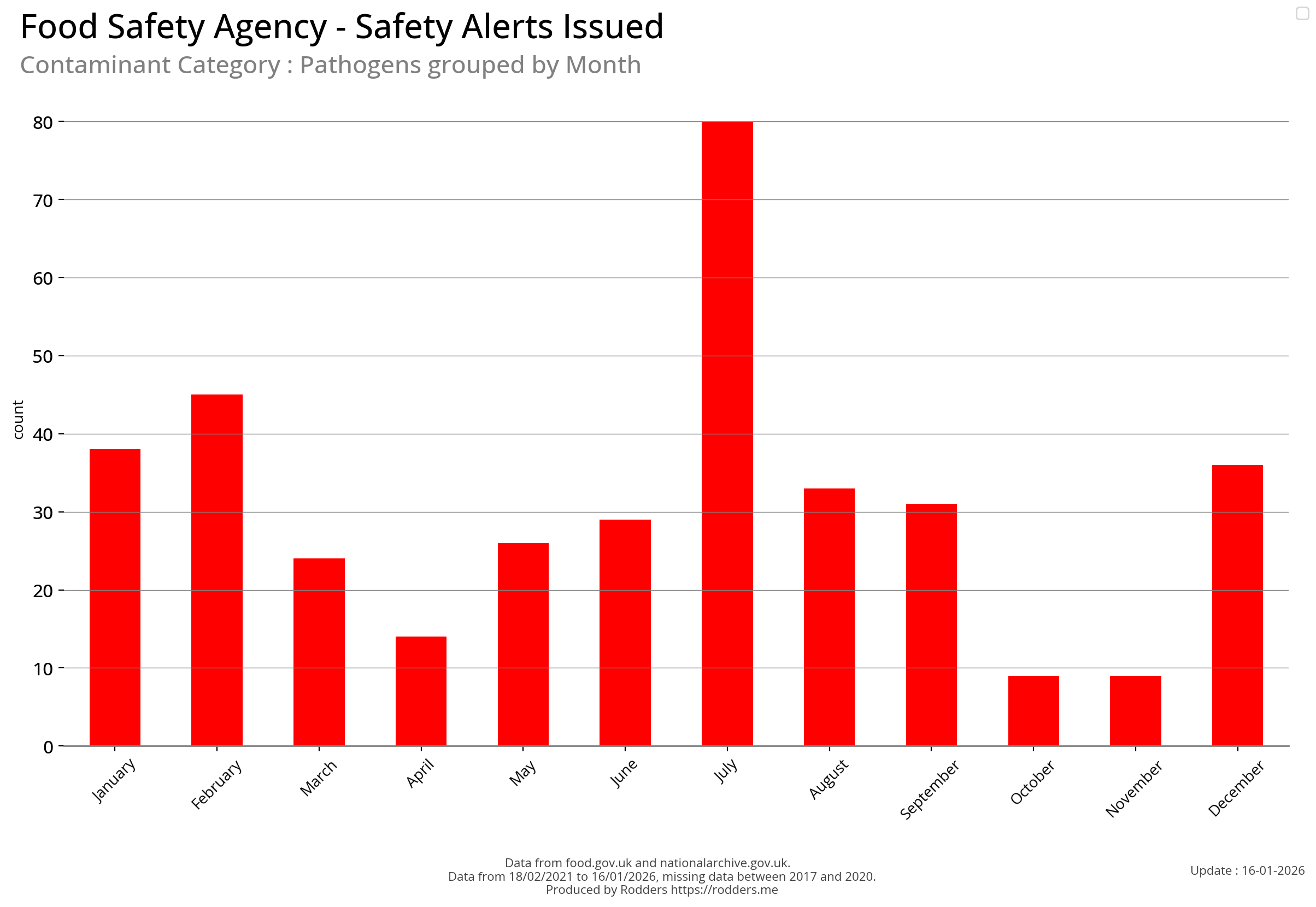
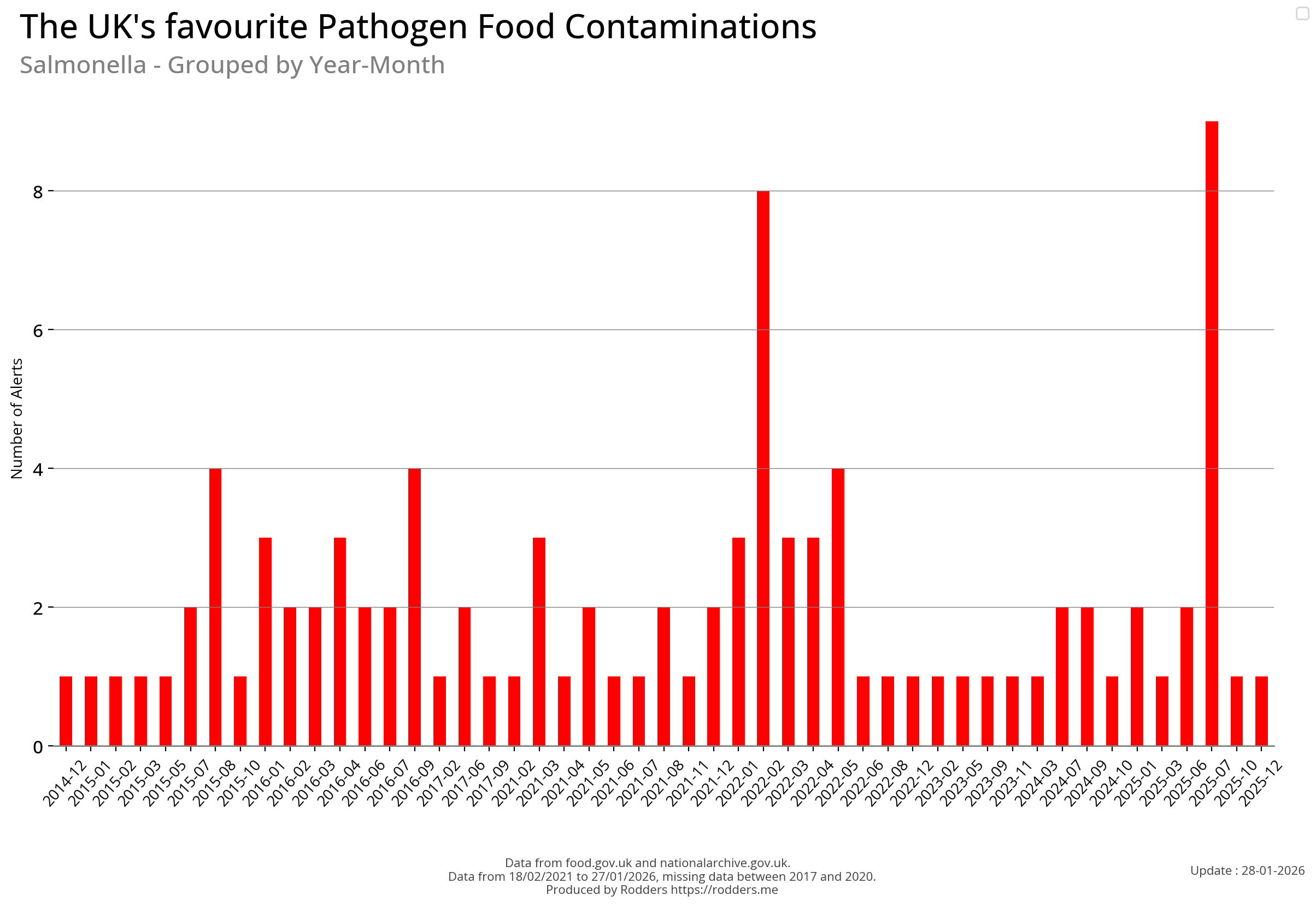
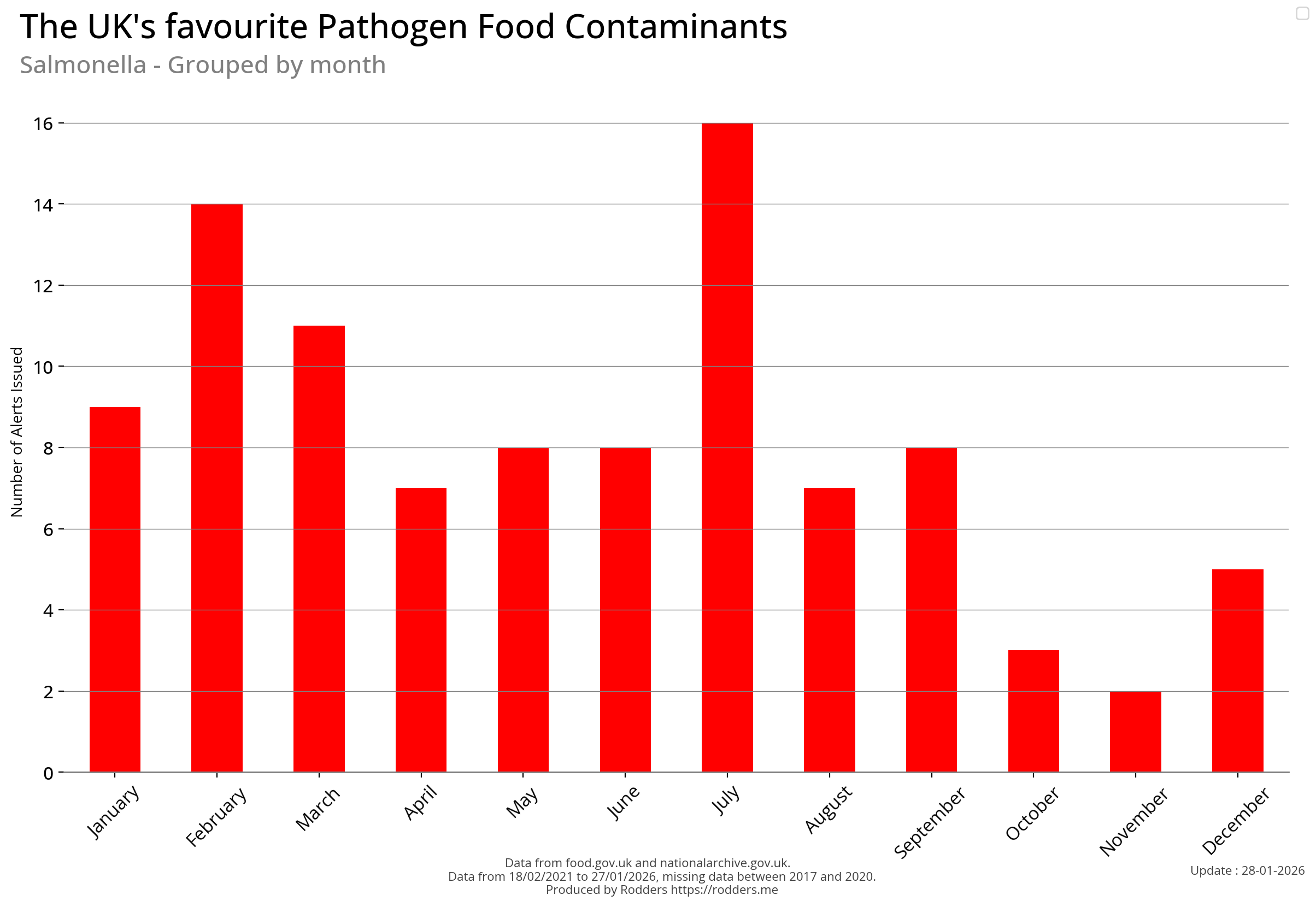
Time Series Visualisations of Pathogen Safety Alerts
Top
Time Series Visualizations of Pathogen Distribution and Common Affected Foods
Salmonella
Salmonella is a genus of rod-shaped gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Salmonella species are non-spore-forming, predominantly motile enterobacteria with cell diameters between about 0.7 and 1.5 μm, lengths from 2 to 5 μm, and peritrichous flagella. They are chemotrophs, obtaining their energy from oxidation and reduction reactions, using organic sources. They are also facultative anaerobes (are capable of adapting to different environmental conditions), and can thrive in an an oxygen environment but also in an anaerobic environment.
Salmonella is a type of bacteria that can cause food poisoning in humans. It is the most common pathogenic contamination in UK Foods.
From a food safety perspective, Salmonella is a significant concern because it can contaminate a wide range of foods and beverages, including:
- Meat: Raw poultry, pork, beef, lamb, and veal are all potential sources of Salmonella.
- Eggs: Salmonella Enteritidis is the most common cause of egg-related illnesses.
- Dairy products: Raw milk, cream, cheese, and ice cream can be contaminated with Salmonella.
- Produce: Fresh fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, sprouts, and leafy greens, can harbor Salmonella.
- Fruits and juices: Contaminated fruit juice, cider, and unpasteurized apple cider can spread the bacteria.
Most Common Foods Contaminated with Salmonella
Top
Temporal Visualisations
Top
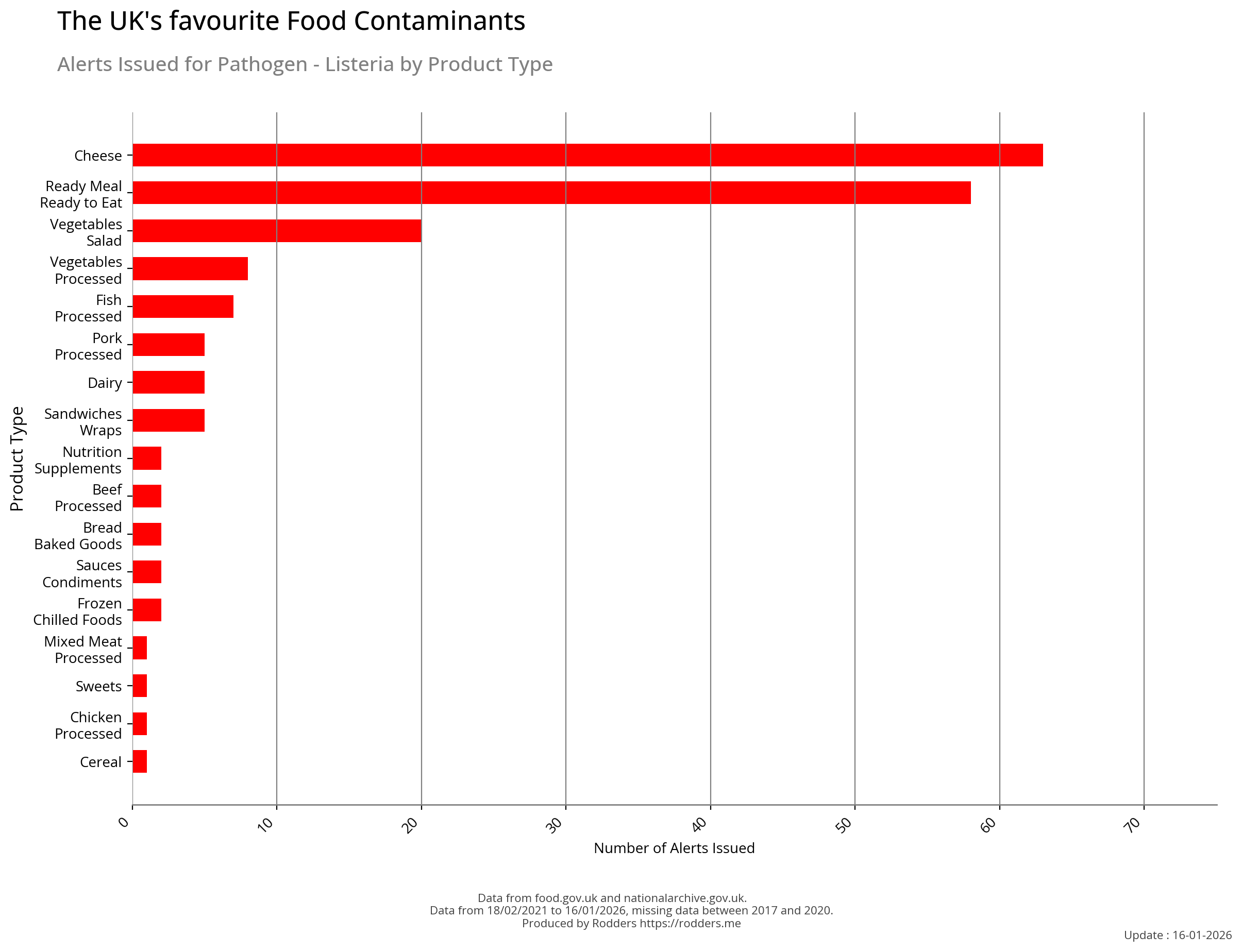
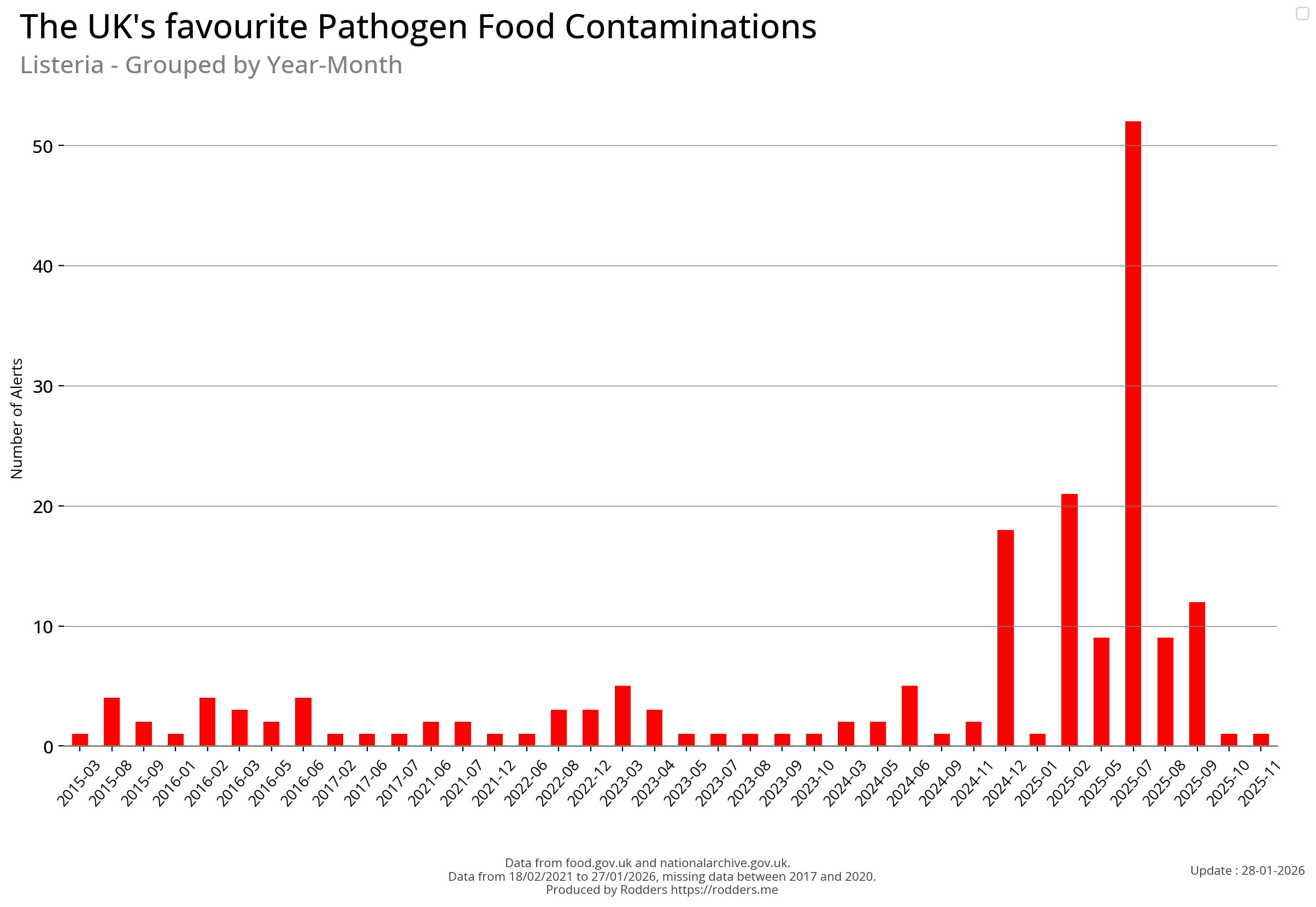
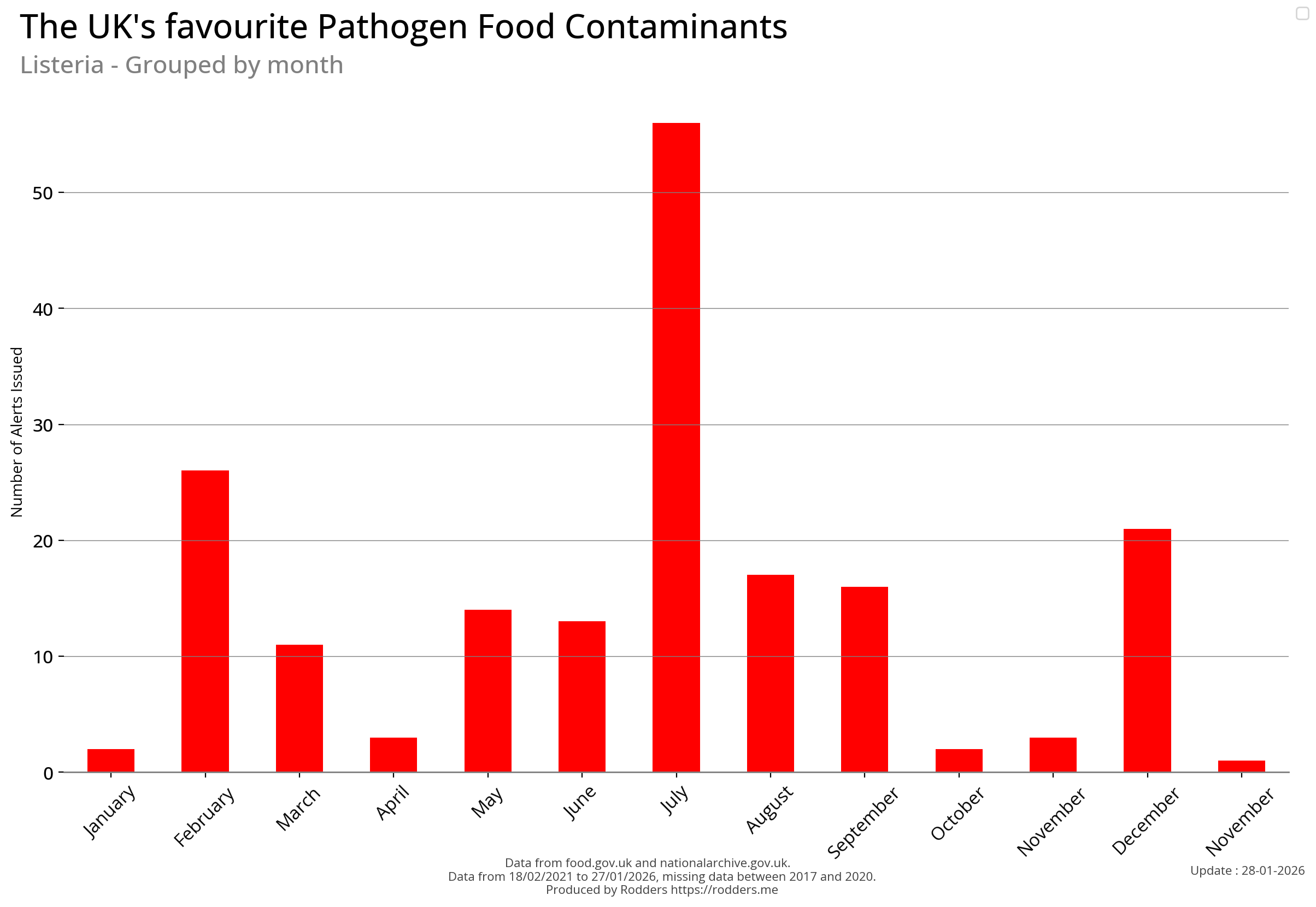
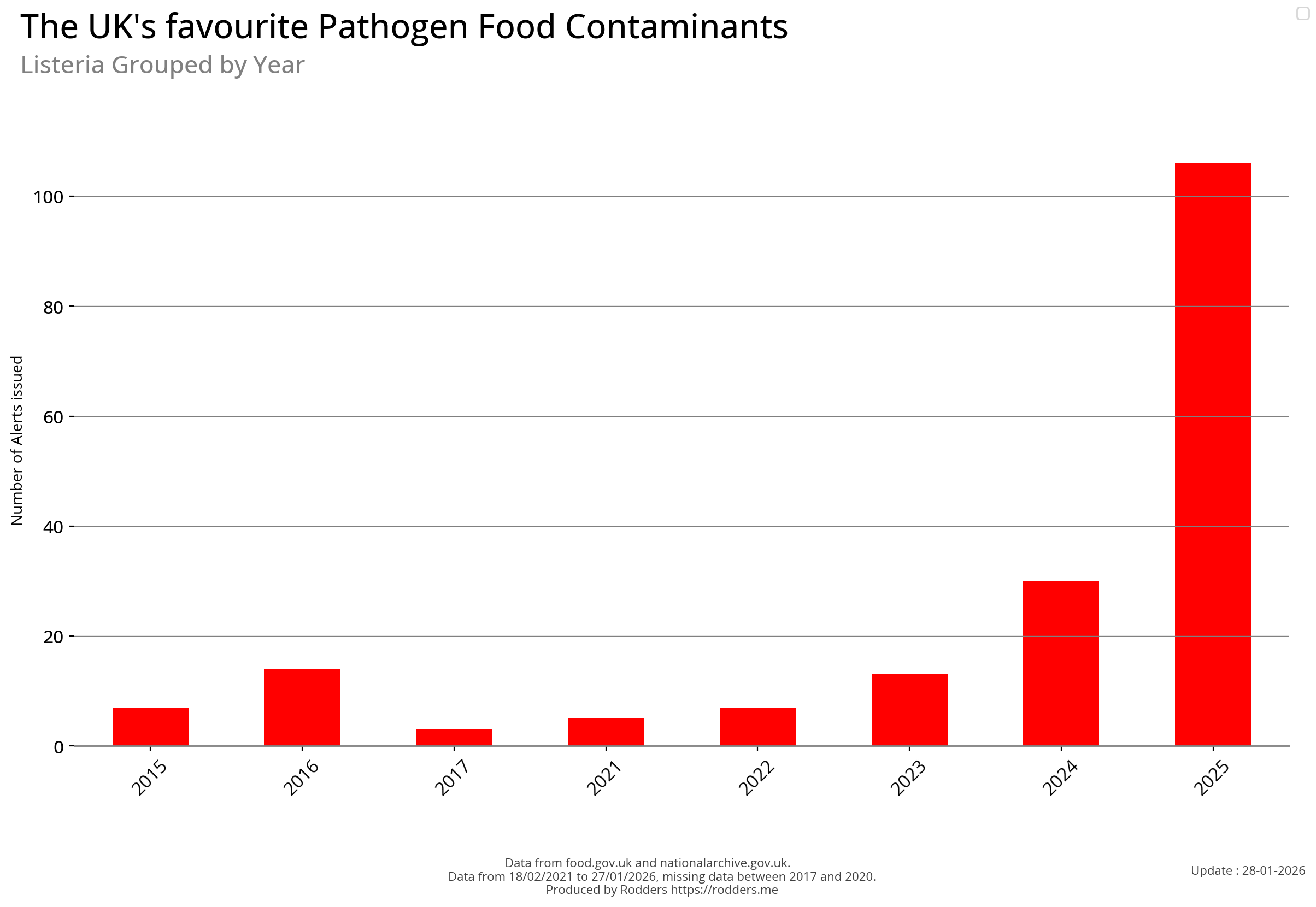
Listeria
Listeria is a genus of bacteria that acts as an intracellular parasite in mammals. Until 1992, 10 species were known, each containing two subspecies. By 2024, 28 species had been identified. The genus is named in honour of the British pioneer of sterile surgery Joseph Lister. Listeria species are Gram-positive, rod-shaped, and facultatively anaerobic, and do not produce endospores. The major human pathogen in the genus Listeria is L. monocytogenes. It is usually the causative agent of the relatively rare bacterial disease listeriosis, an infection caused by eating food contaminated with the bacteria. Listeriosis can cause serious illness in pregnant women, newborns, adults with weakened immune systems and the elderly, and may cause gastroenteritis in others who have been severely infected. Listeriosis is a serious disease for humans; the overt form of the disease has a case-fatality rate of around 20-30%.
Most Common Foods Contaminated with Listeria
Top
Temporal Visualisations
Top
Clostridium Botulinum
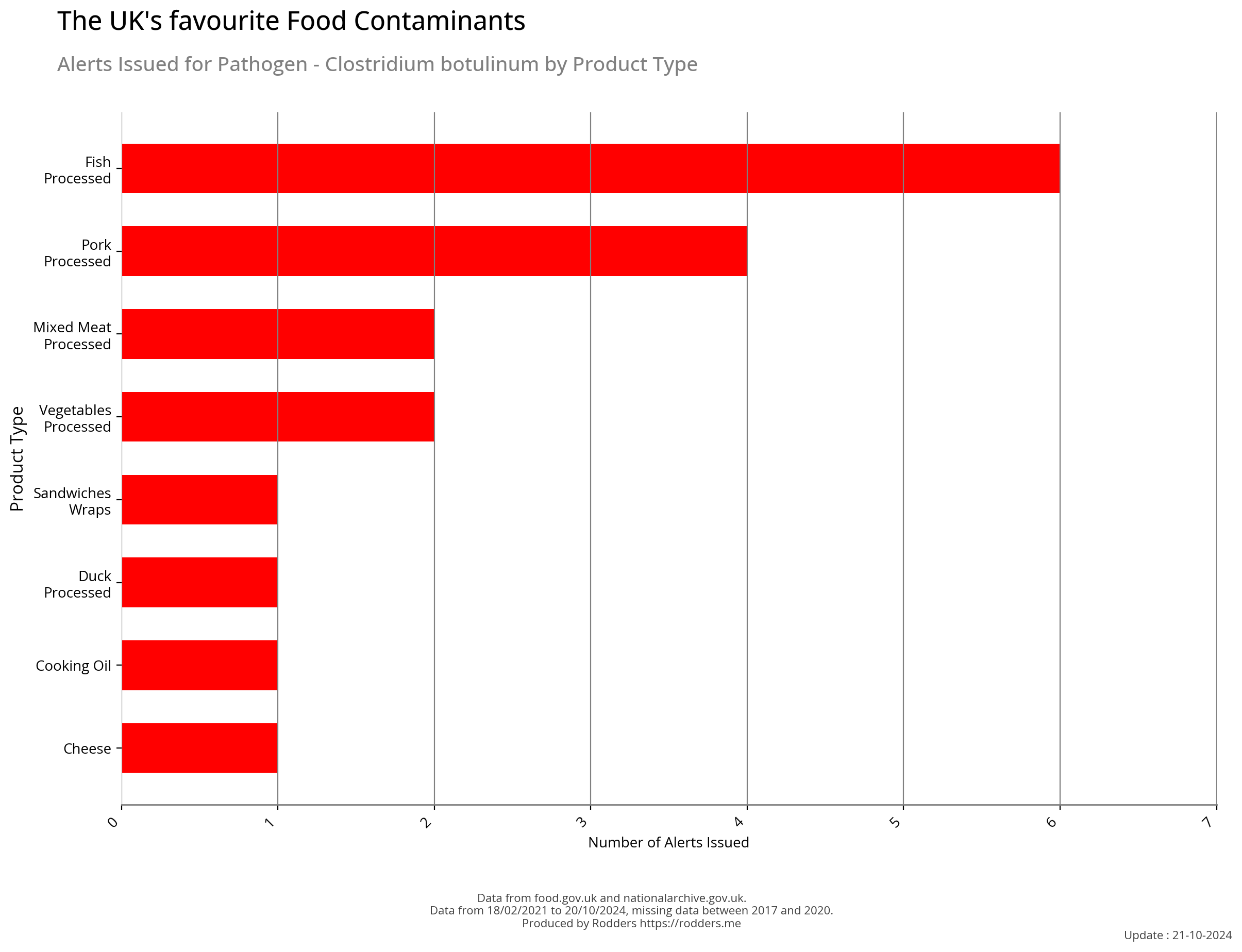
Clostridium botulinum is a gram-positive, rod-shaped, anaerobic, spore-forming, motile bacterium with the ability to produce botulinum toxin, which is a neurotoxin. C. botulinum is a diverse group of pathogenic bacteria. Initially, they were grouped together by their ability to produce botulinum toxin and are now known as four distinct groups, C. botulinum groups I-IV. Along with some strains of Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium baratii, these bacteria all produce the toxin.
Botulinum toxin can cause botulism, a severe flaccid paralytic disease in humans and other animals, and is the most potent toxin known to science, natural or synthetic, with a lethal dose of 1.3-2.1 ng/kg in humans. C. botulinum is commonly associated with bulging canned food; bulging, misshapen cans can be due to an internal increase in pressure caused by gas produced by bacteria. C. botulinum is responsible for foodborne botulism, infant botulism, and wound botulism.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clostridium_botulinum
Most common foods contaminated with Clostridium botulinum
Top
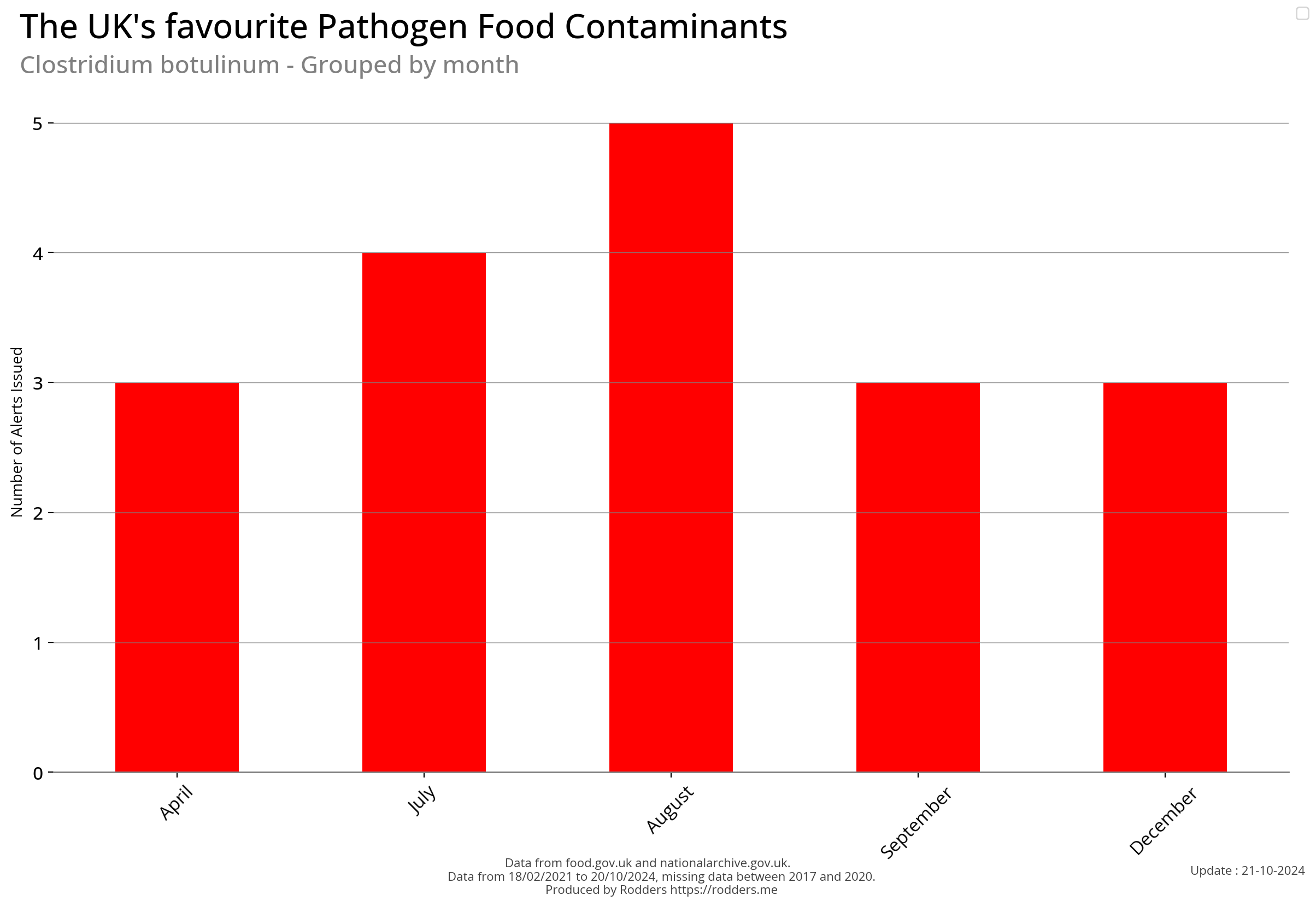
Temporal Visualisations
Top
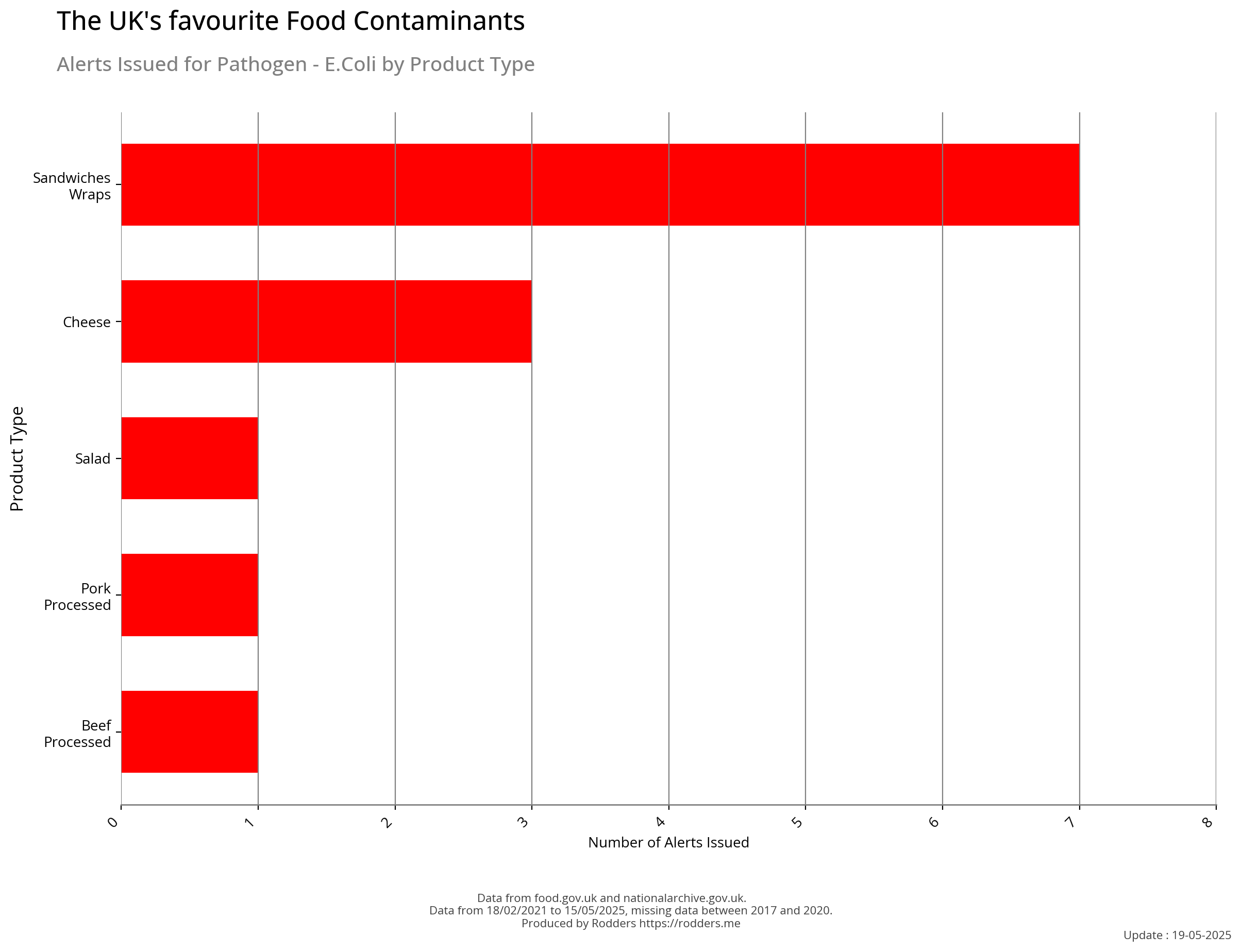
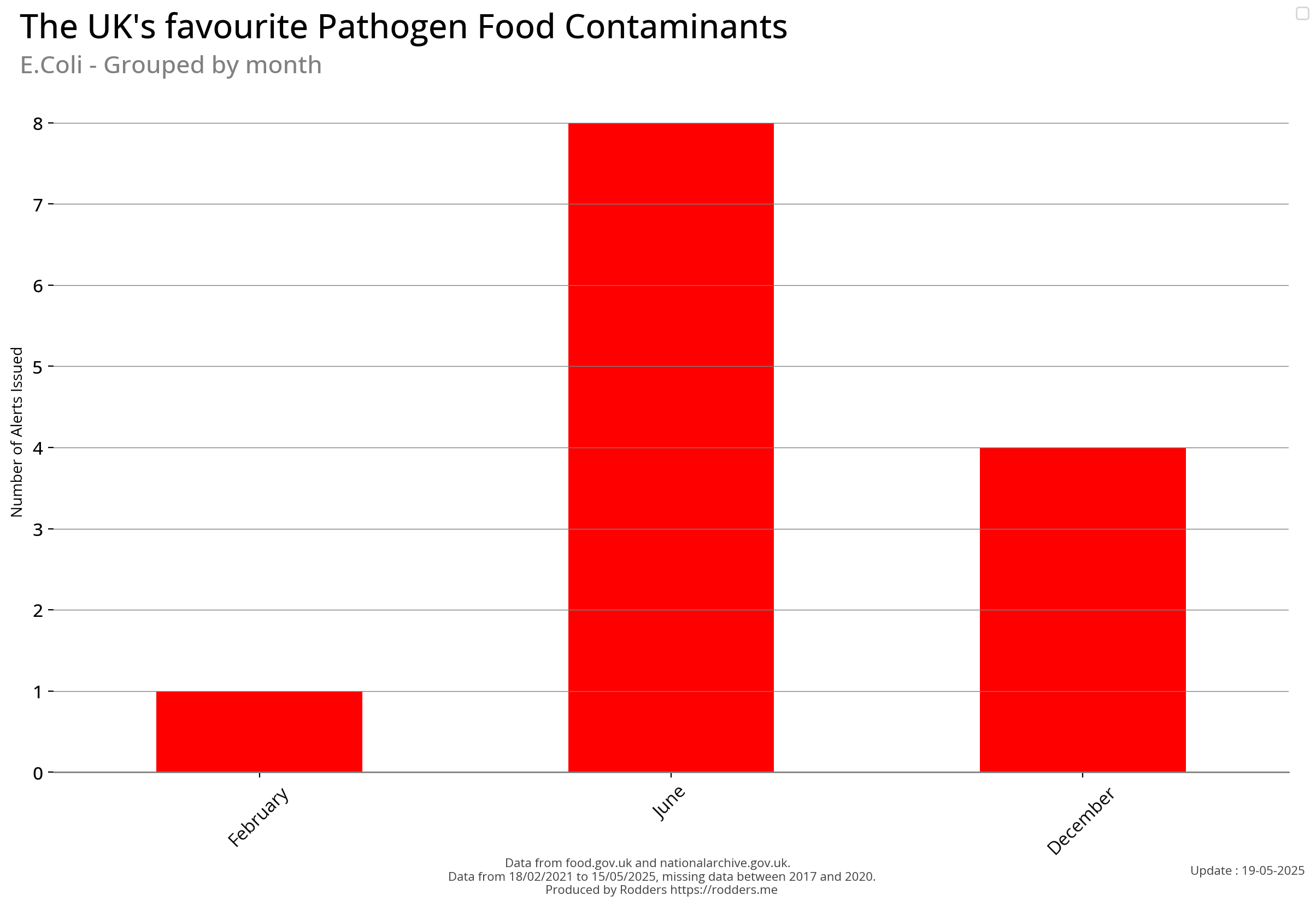
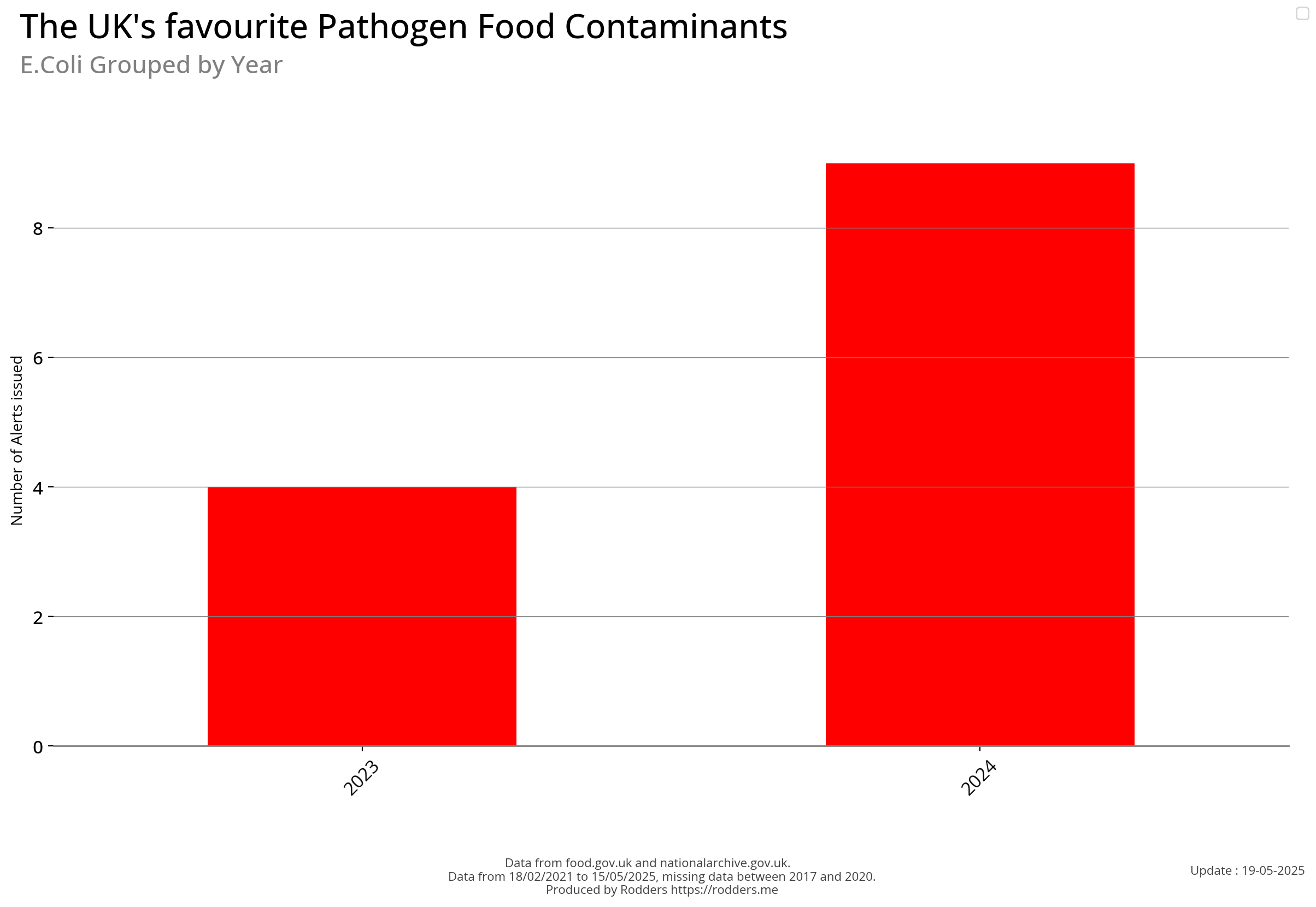
E.coli
Escherichia coli is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes such as EPEC, and ETEC are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut and are harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K₂ or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between E. coli and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship — where both the humans and the E. coli are benefiting each other. E. coli is expelled into the environment within faecal matter.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli
Most Common Foods Contaminated with E.coli
Top
Temporal Visualisations
Top
A Slice Above the Rest: Pathogen Distribution Across Food Types
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
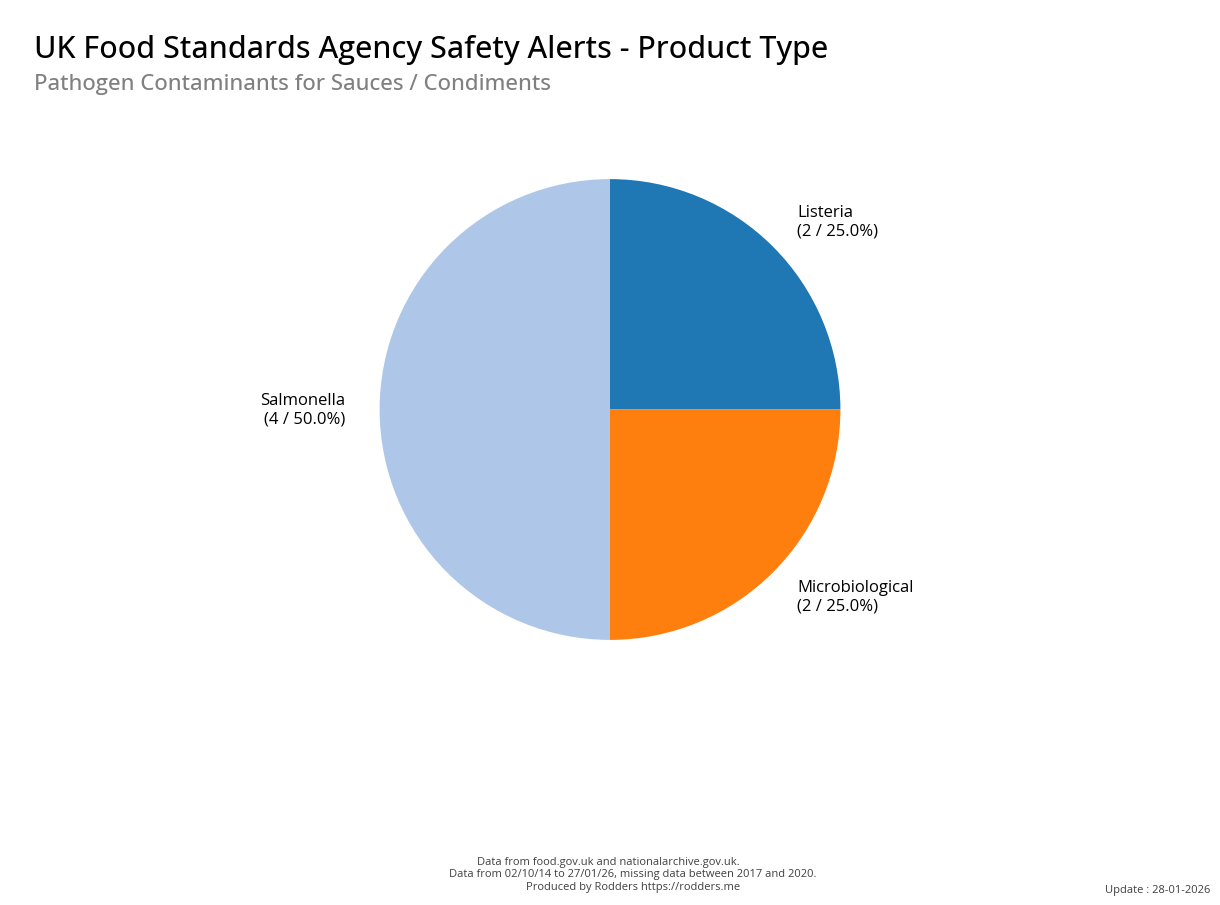
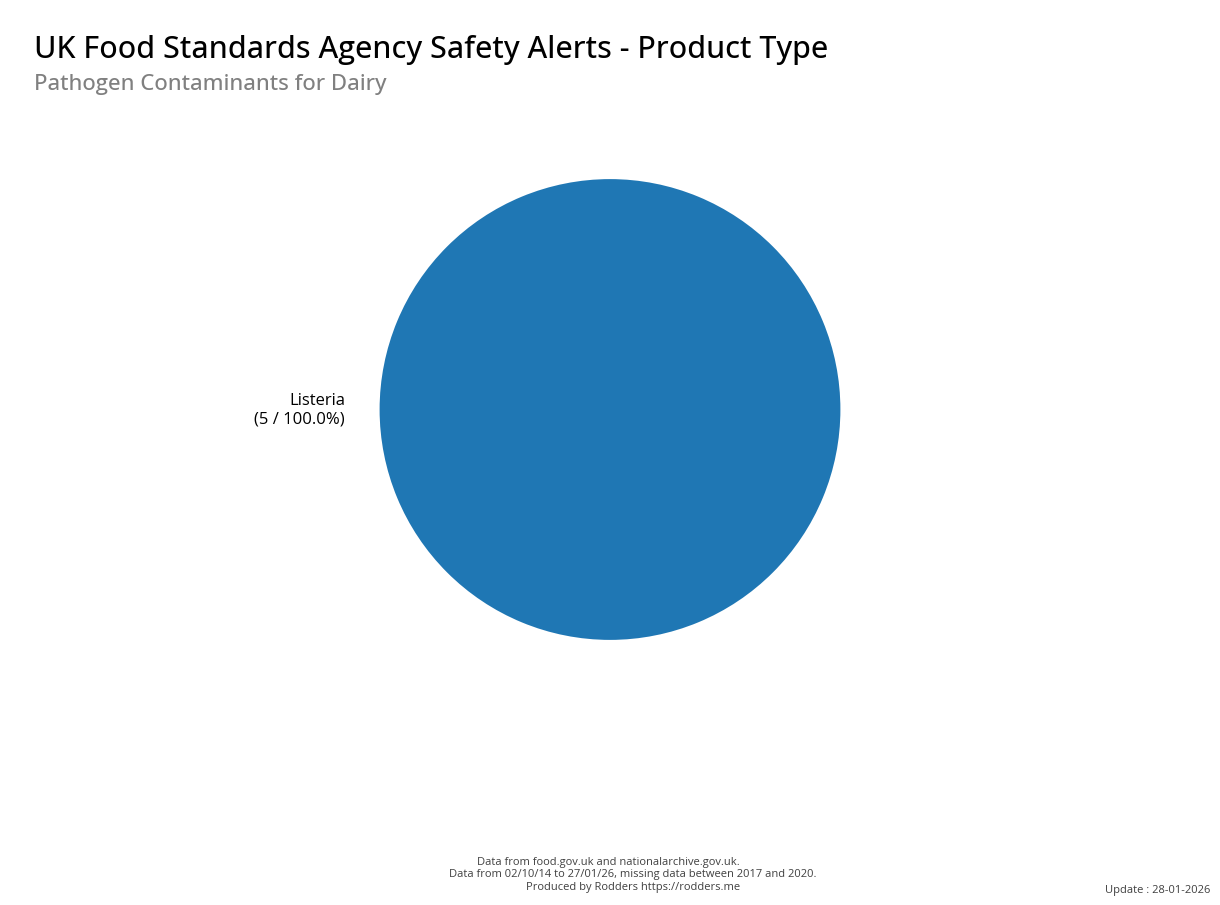
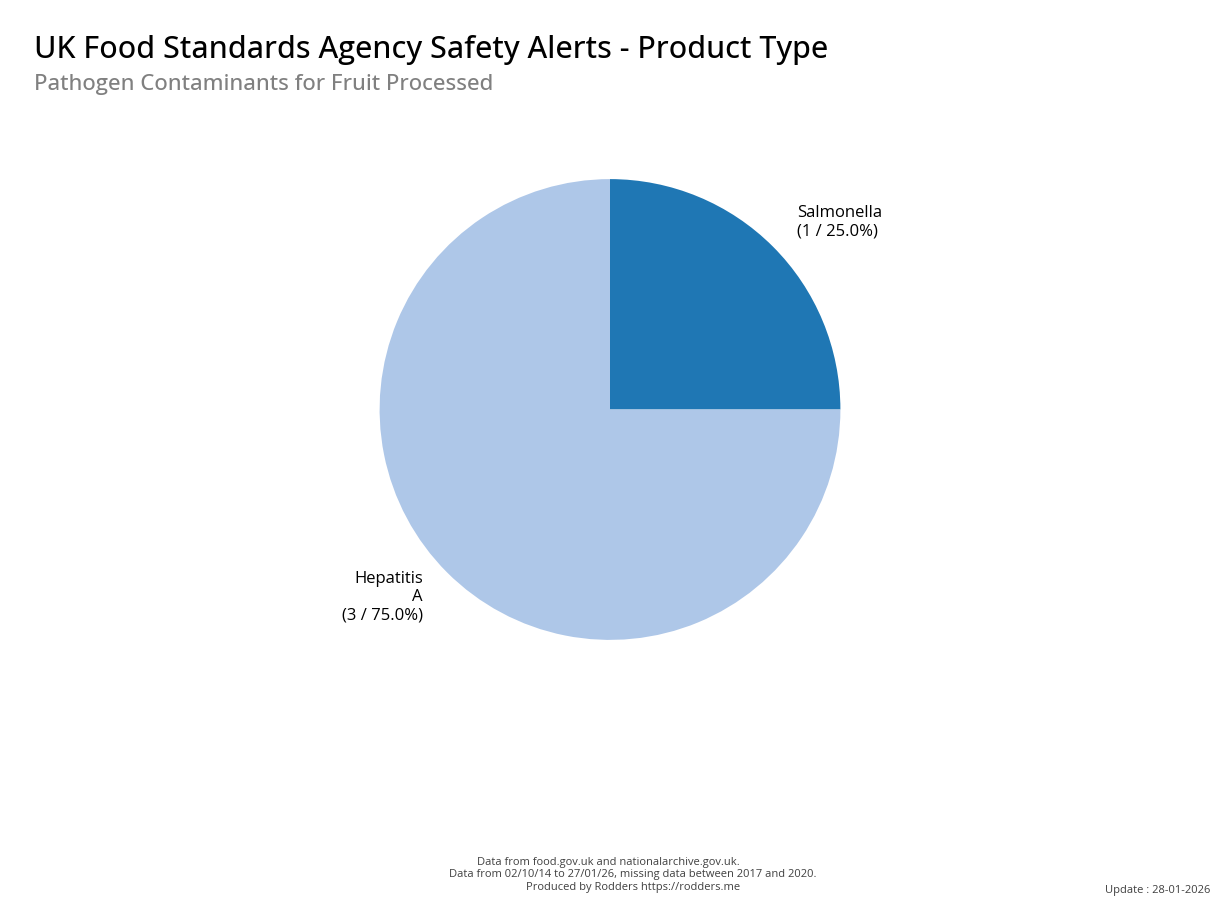
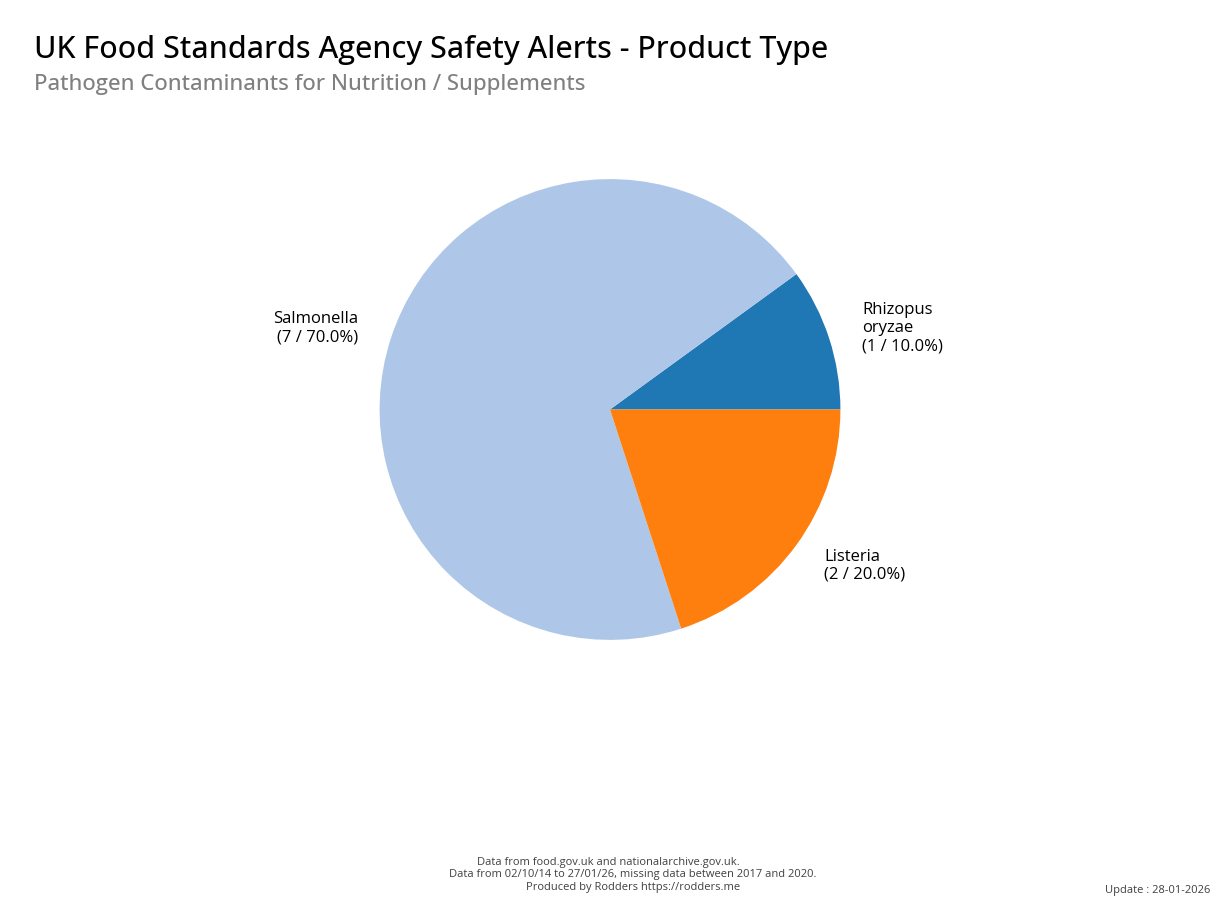
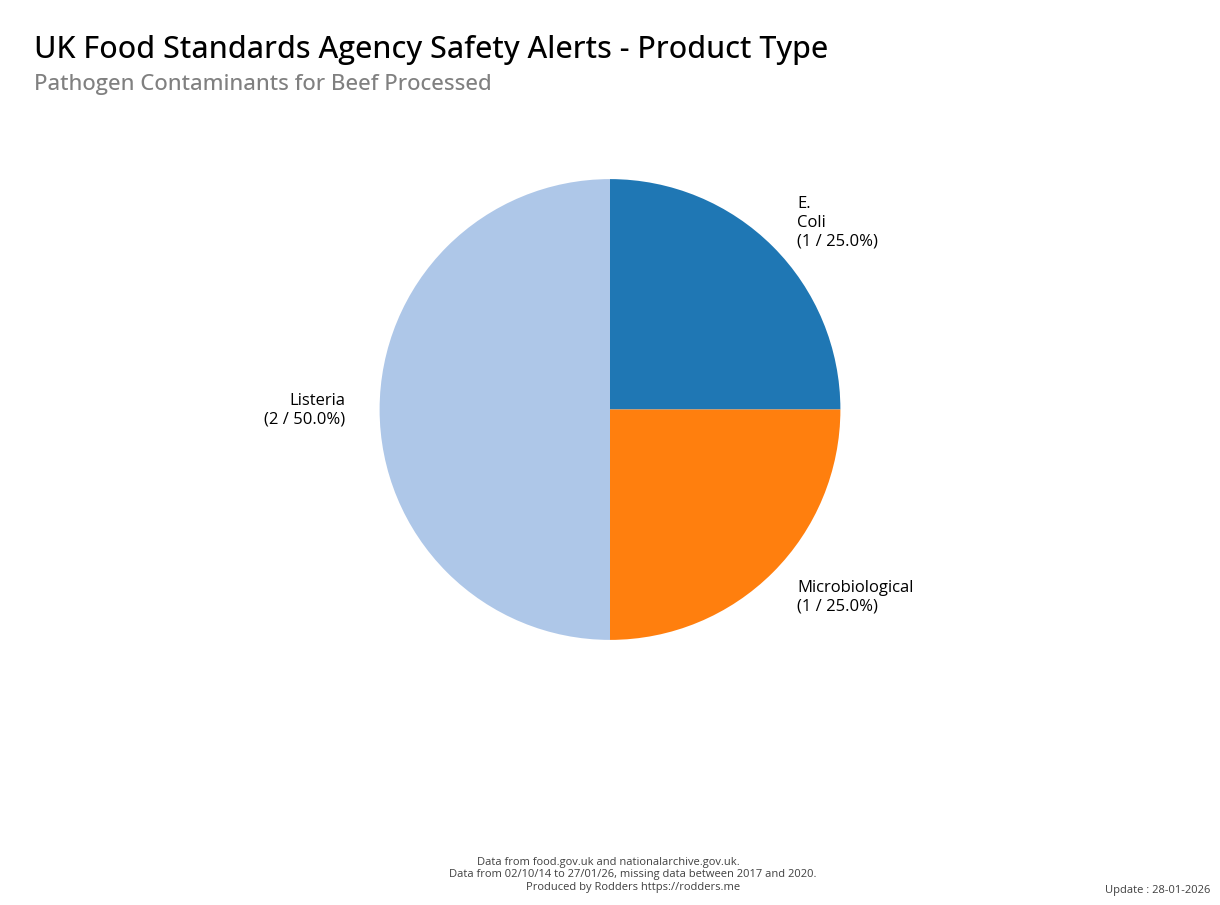
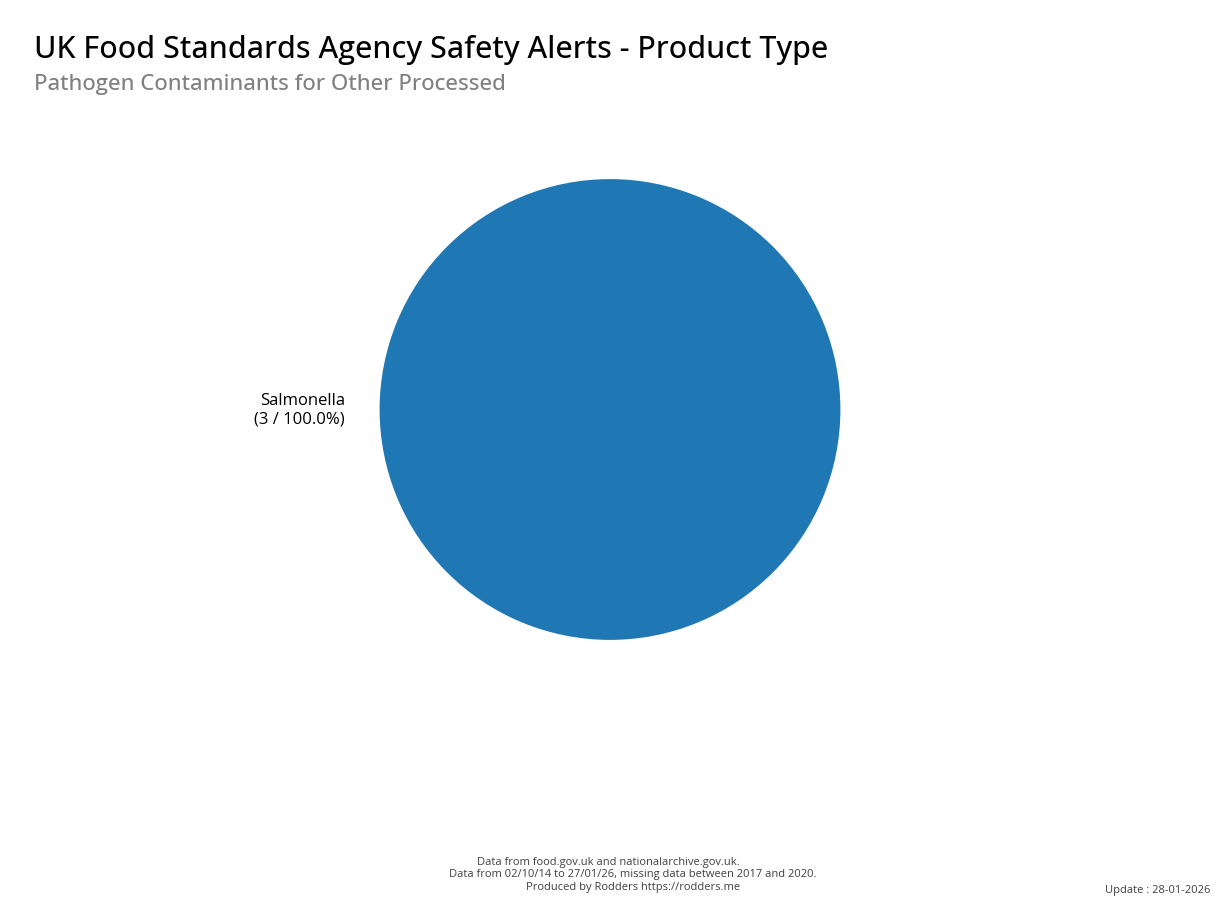
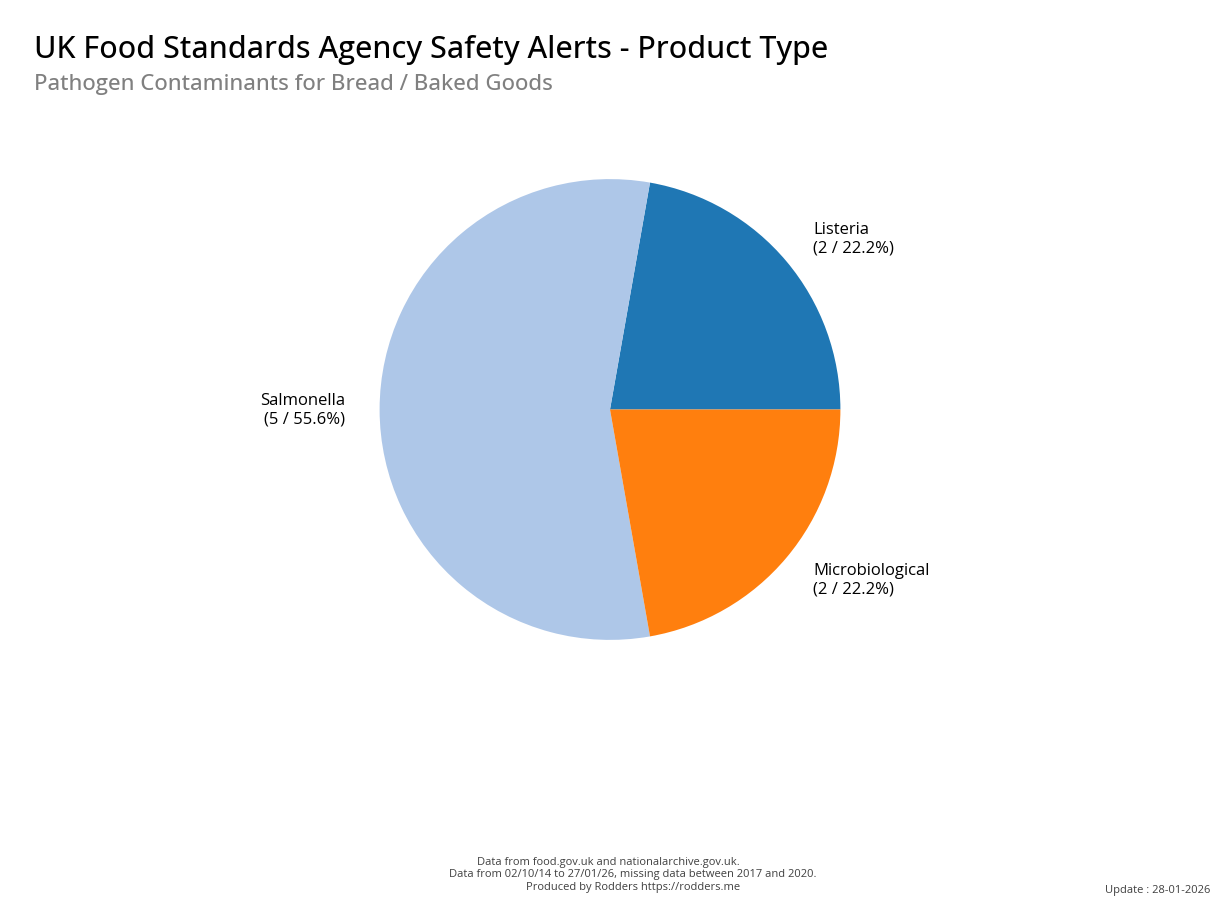
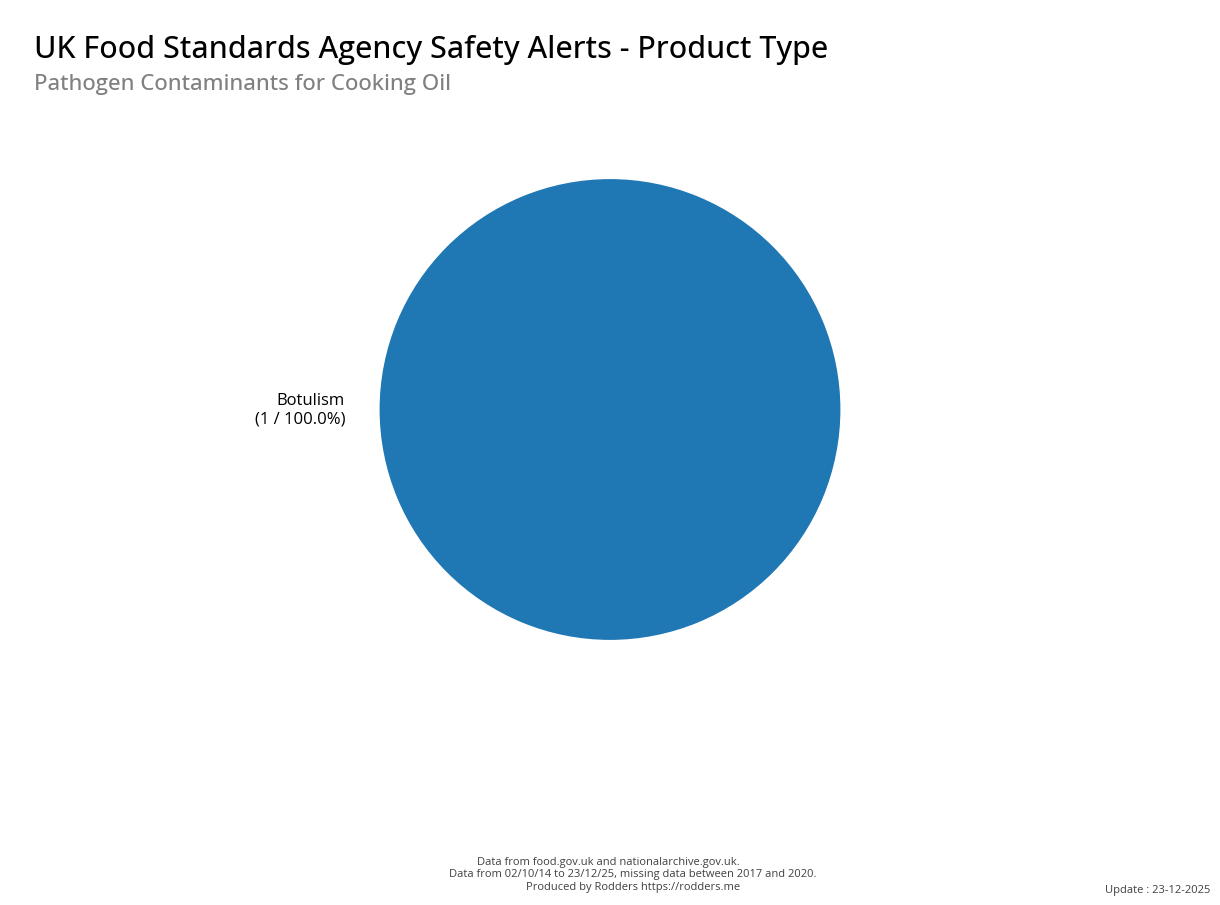
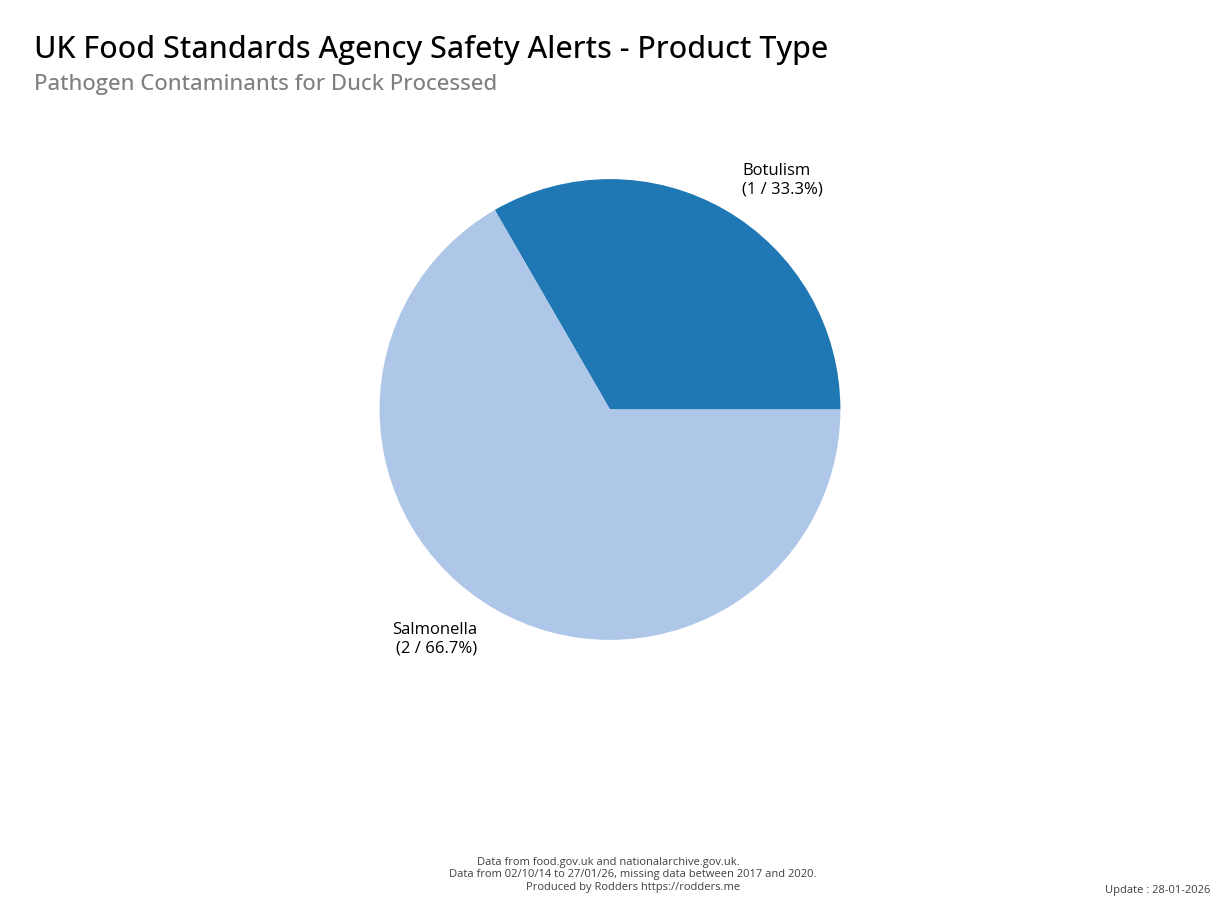
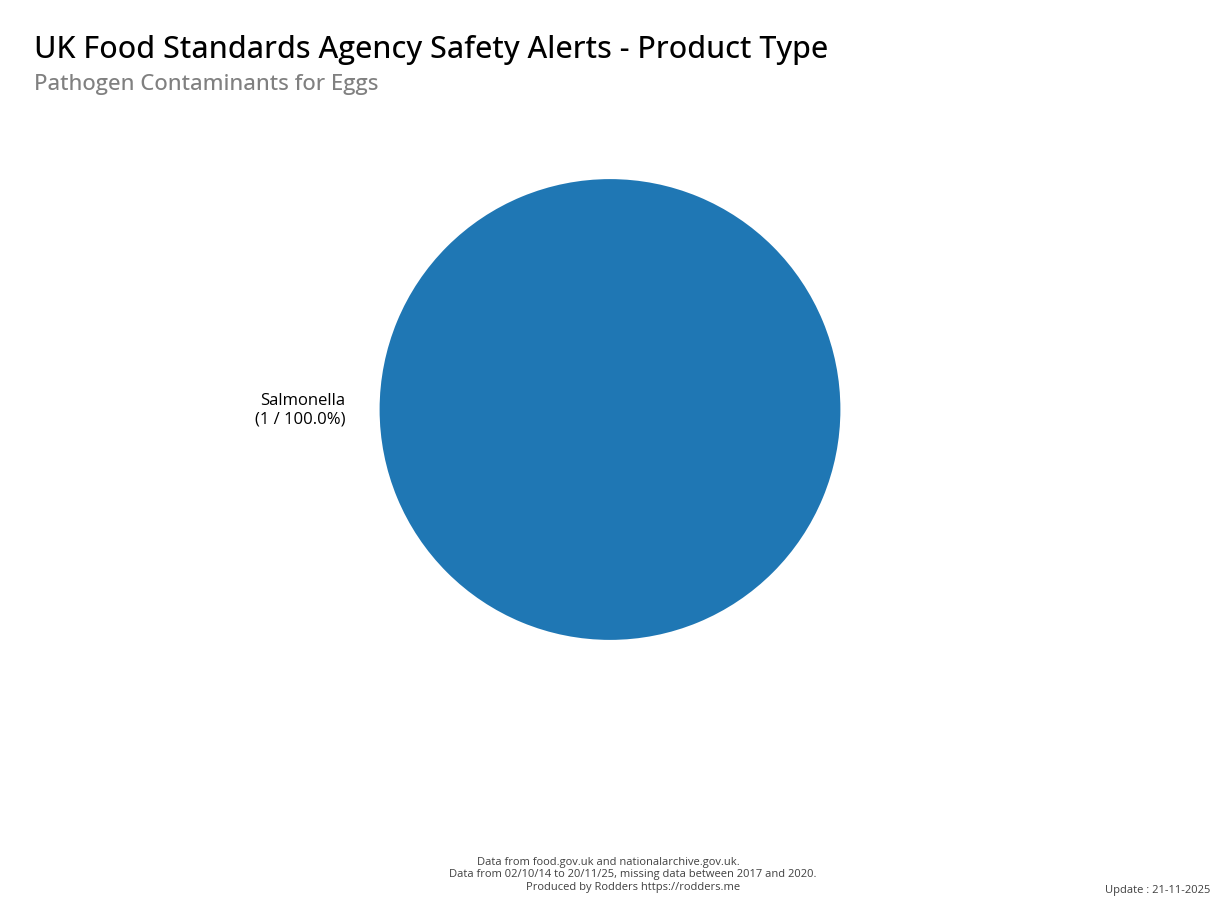
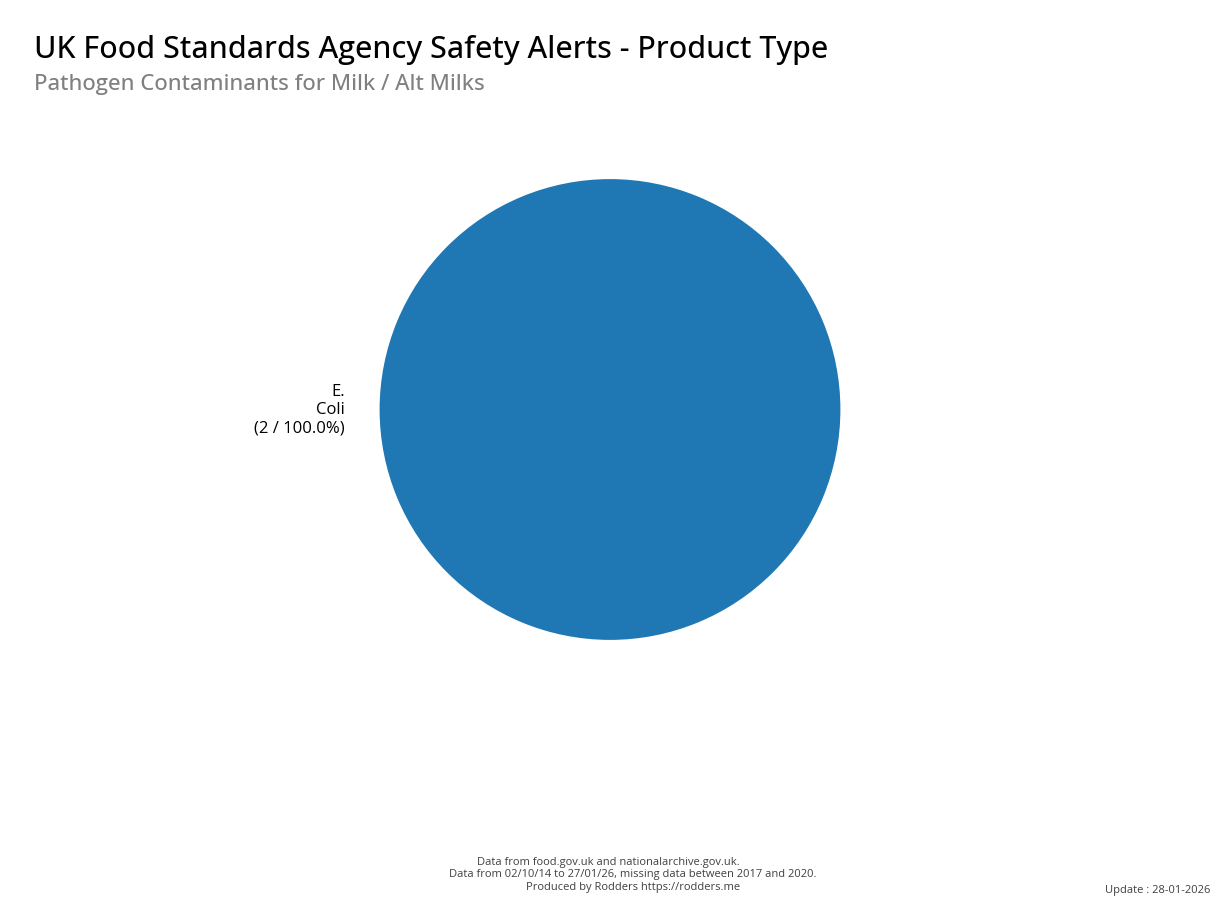
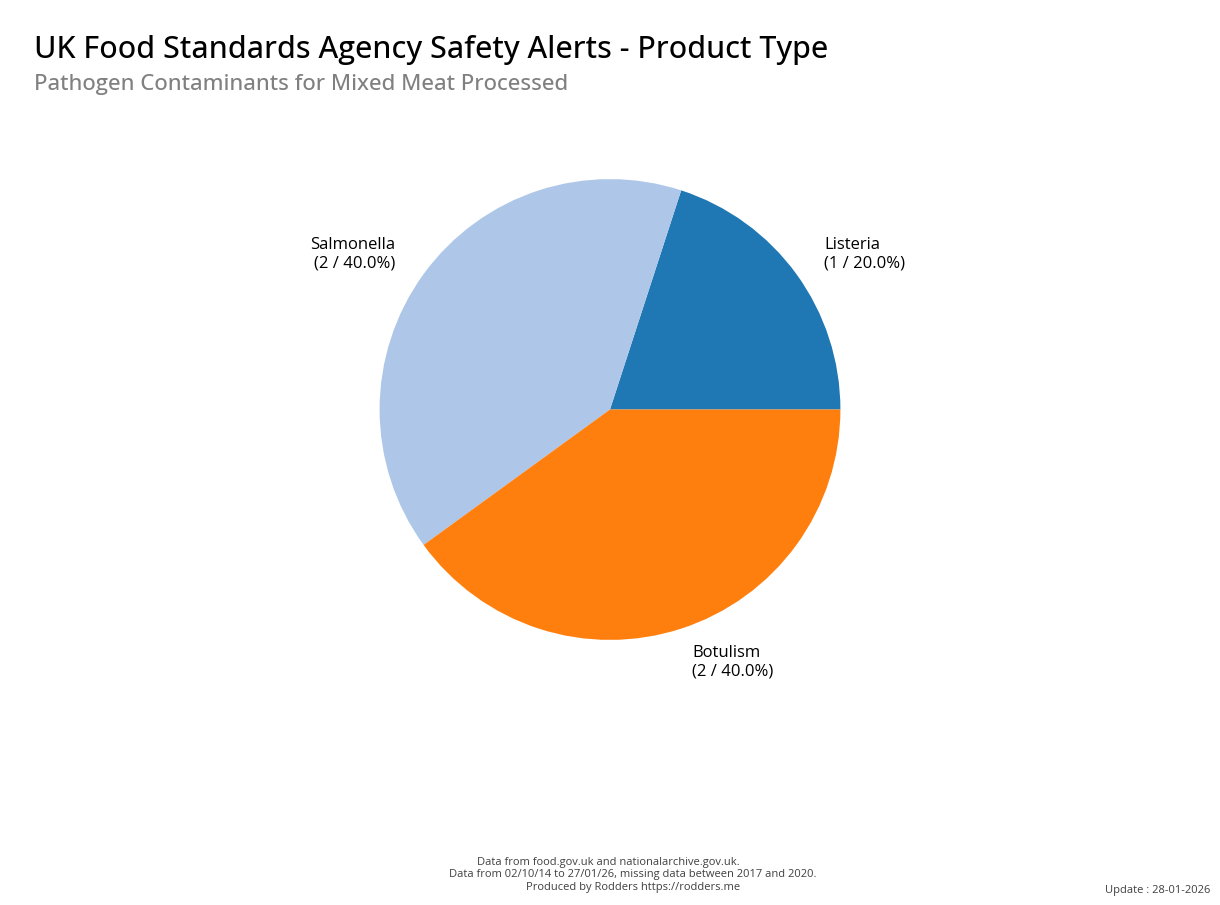
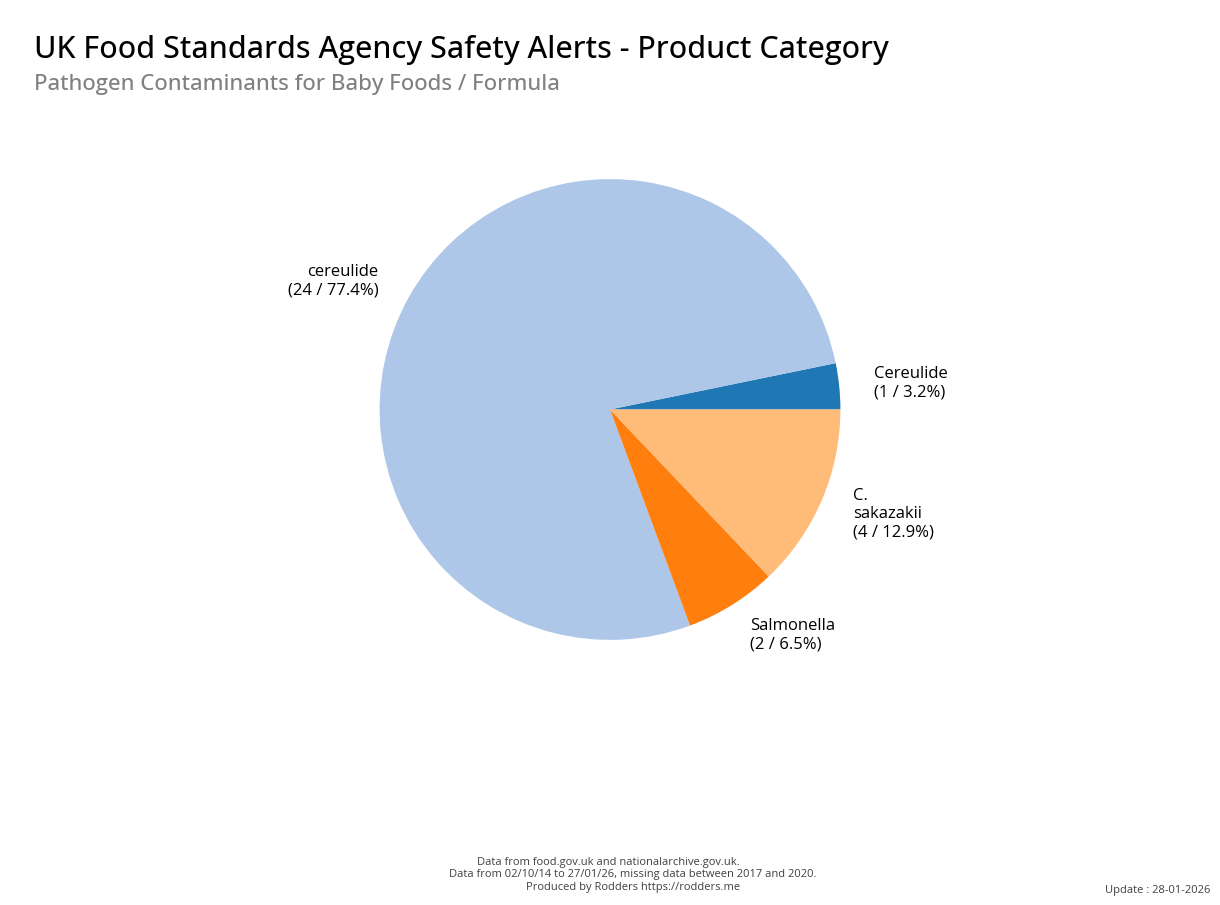
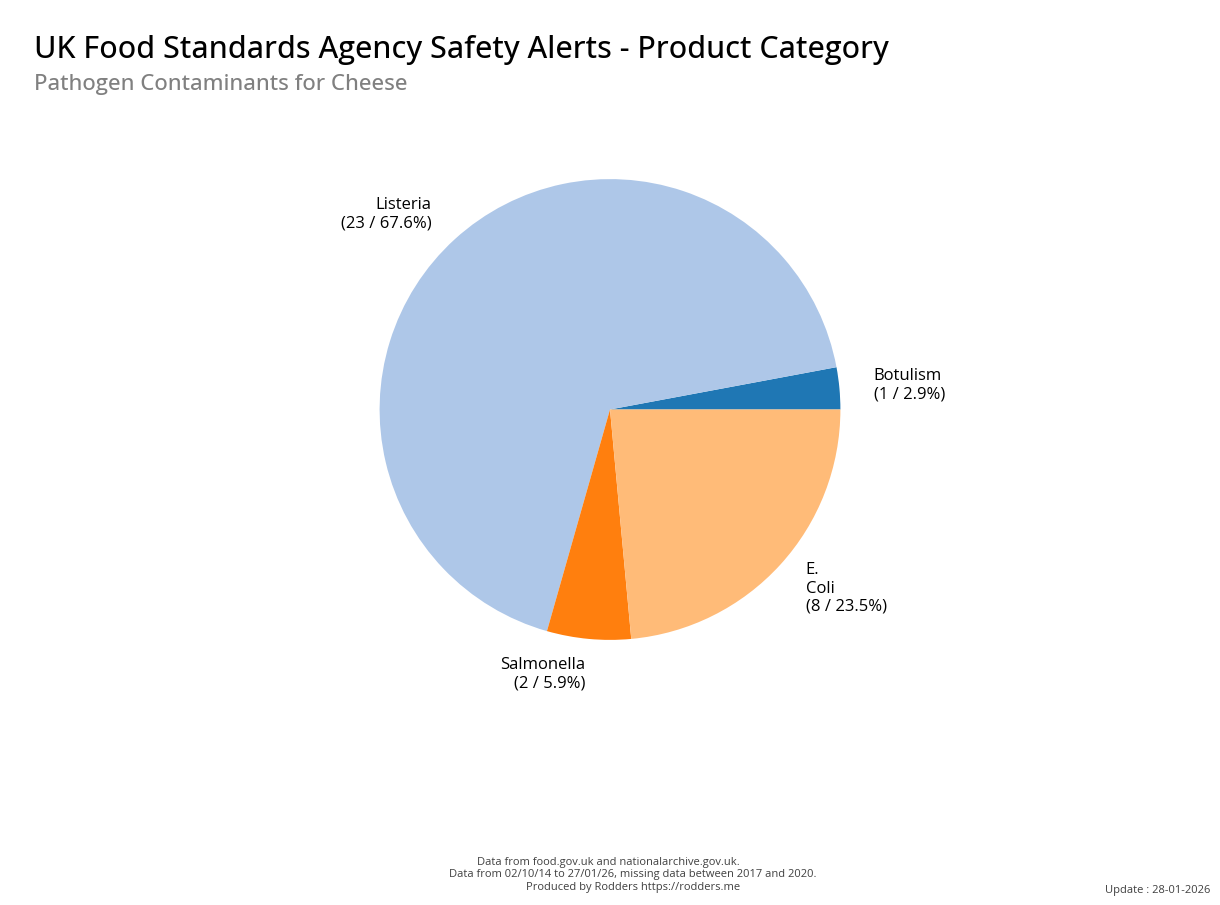
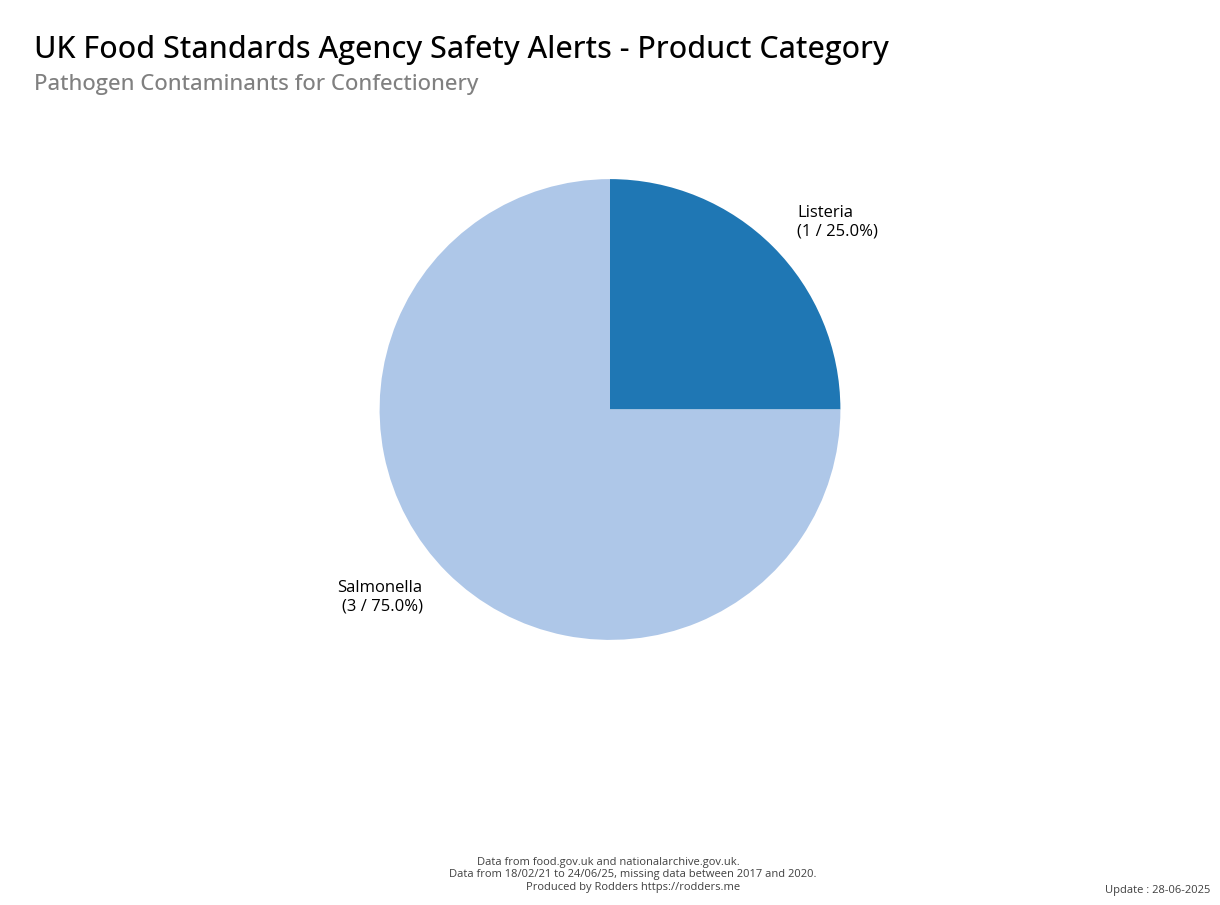
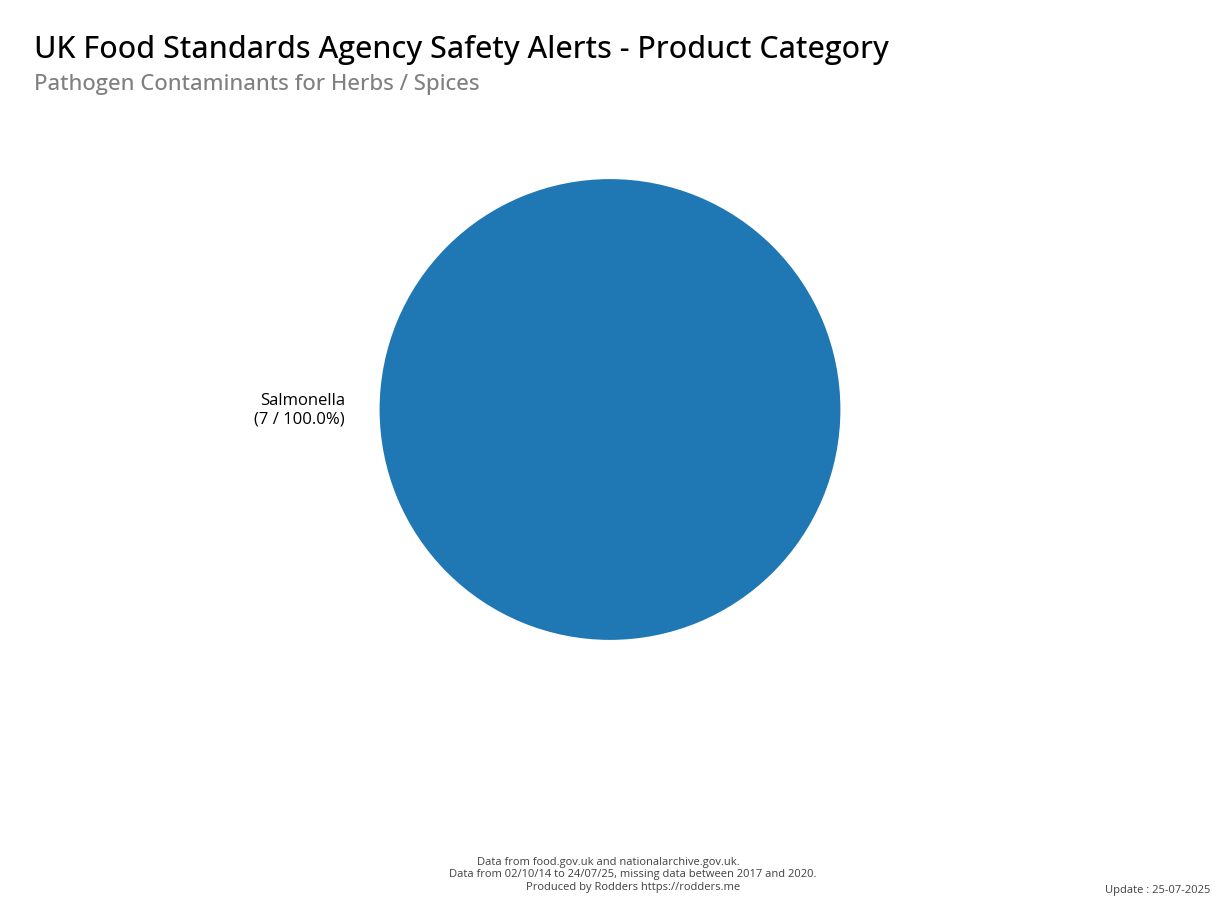
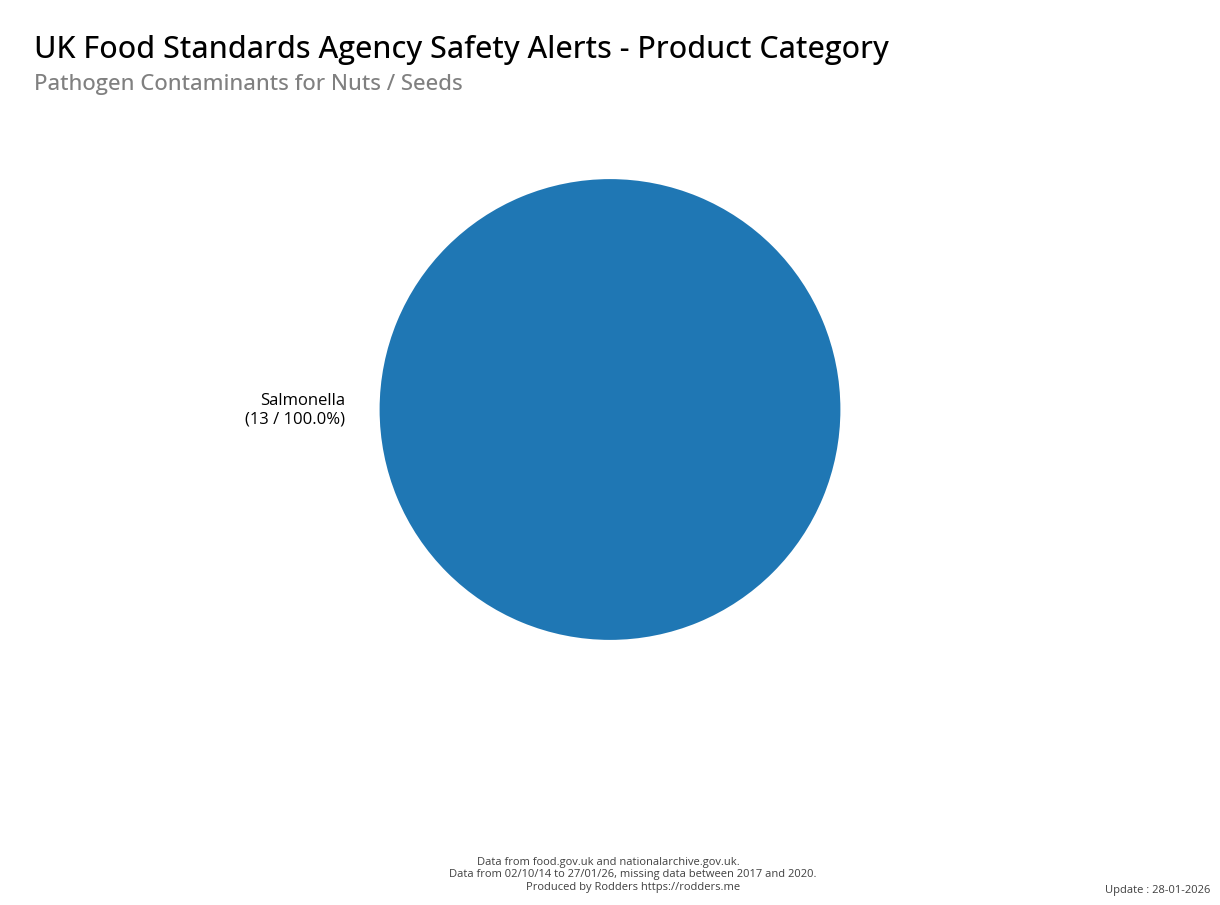
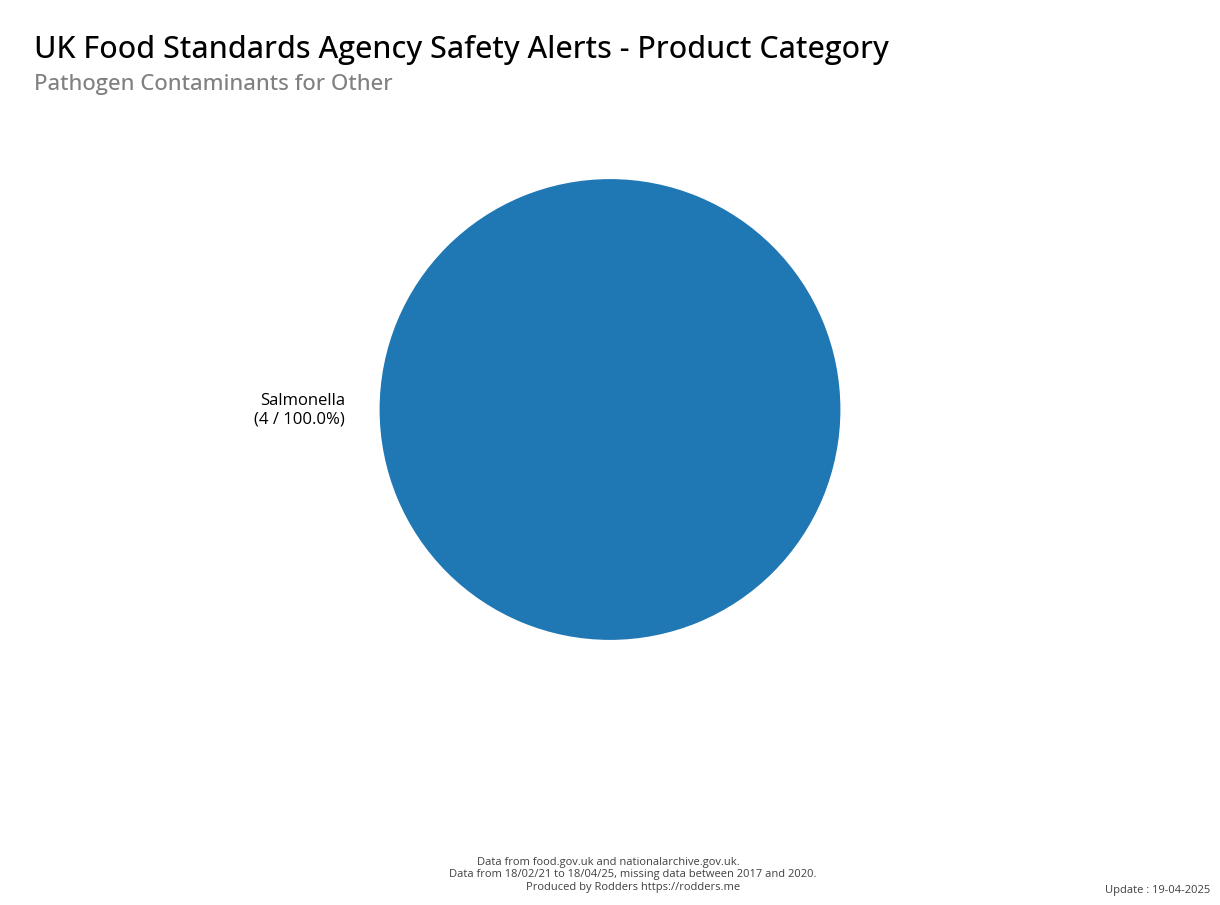
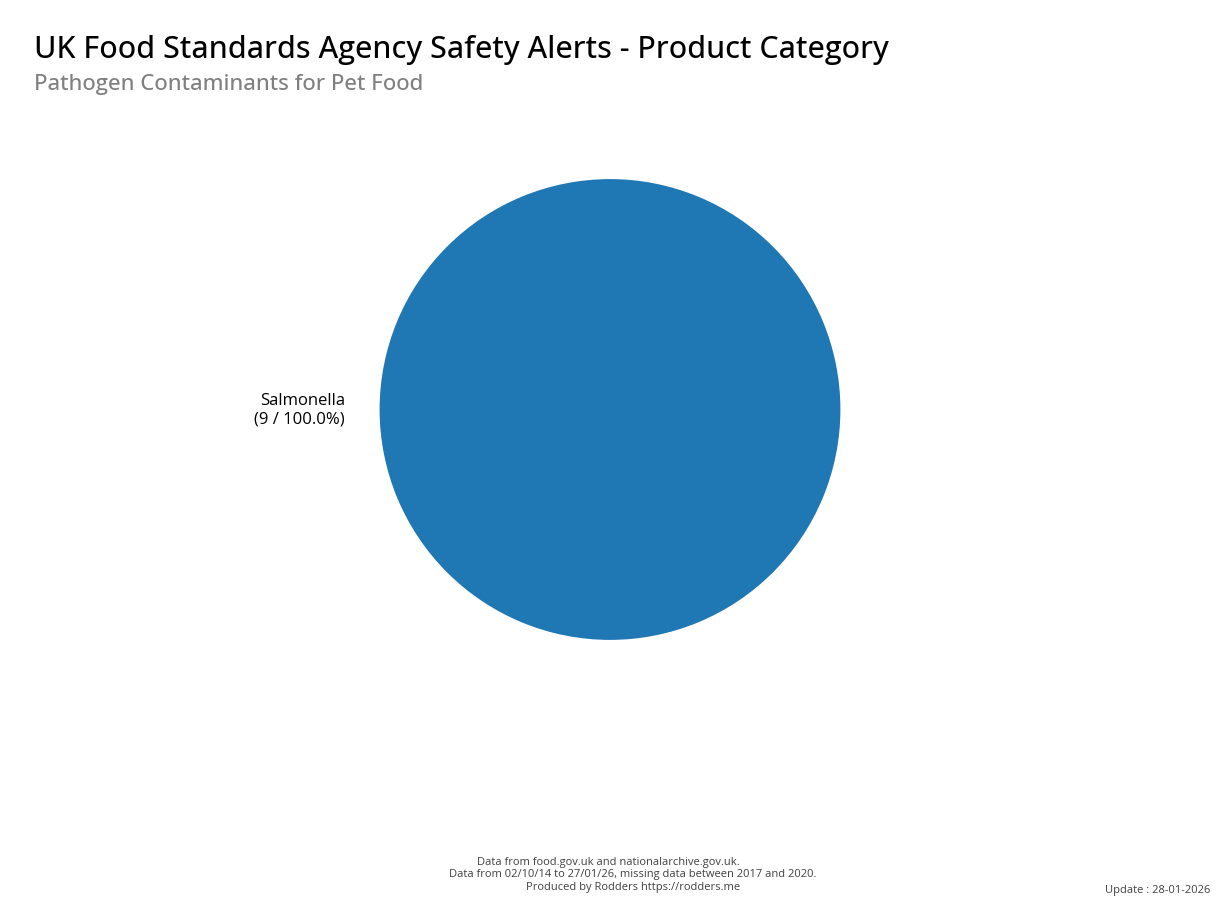
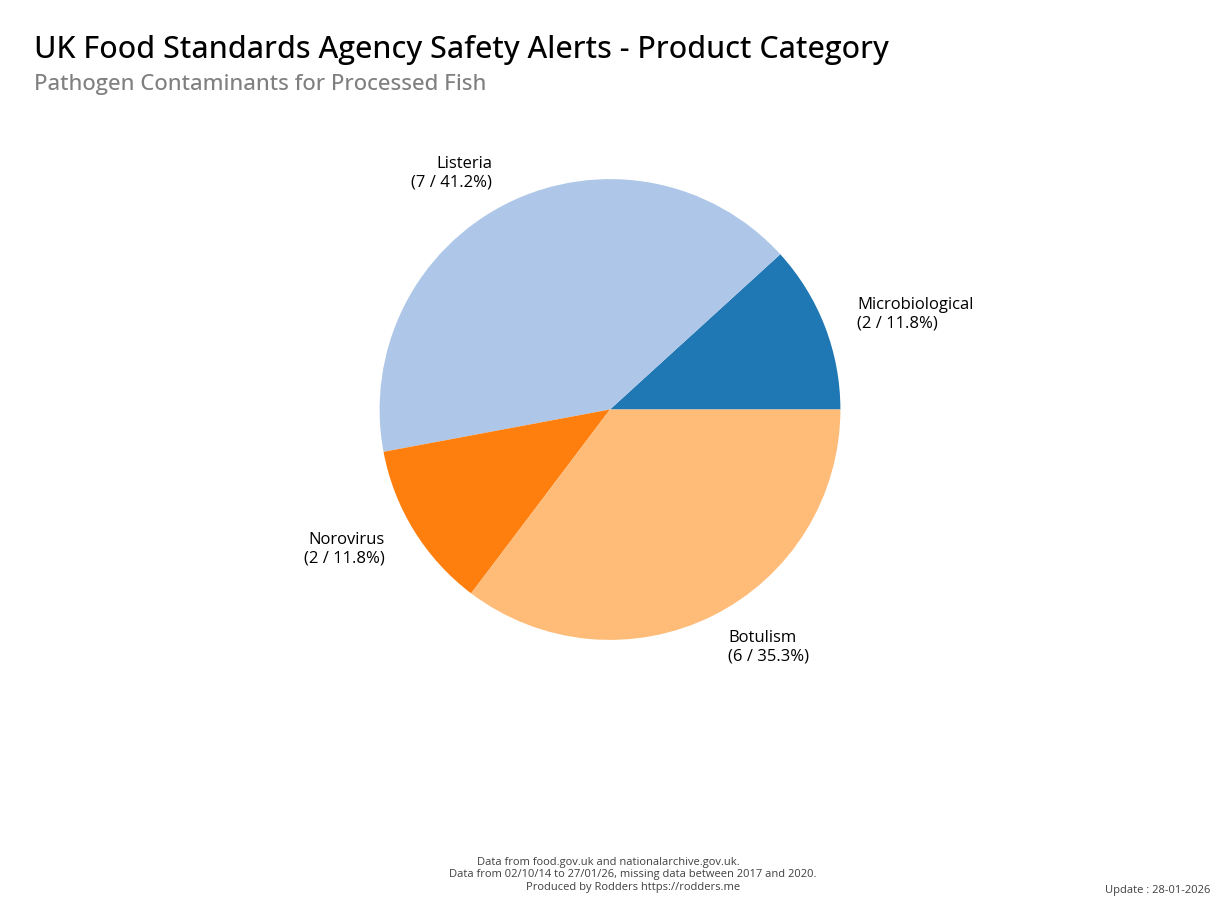
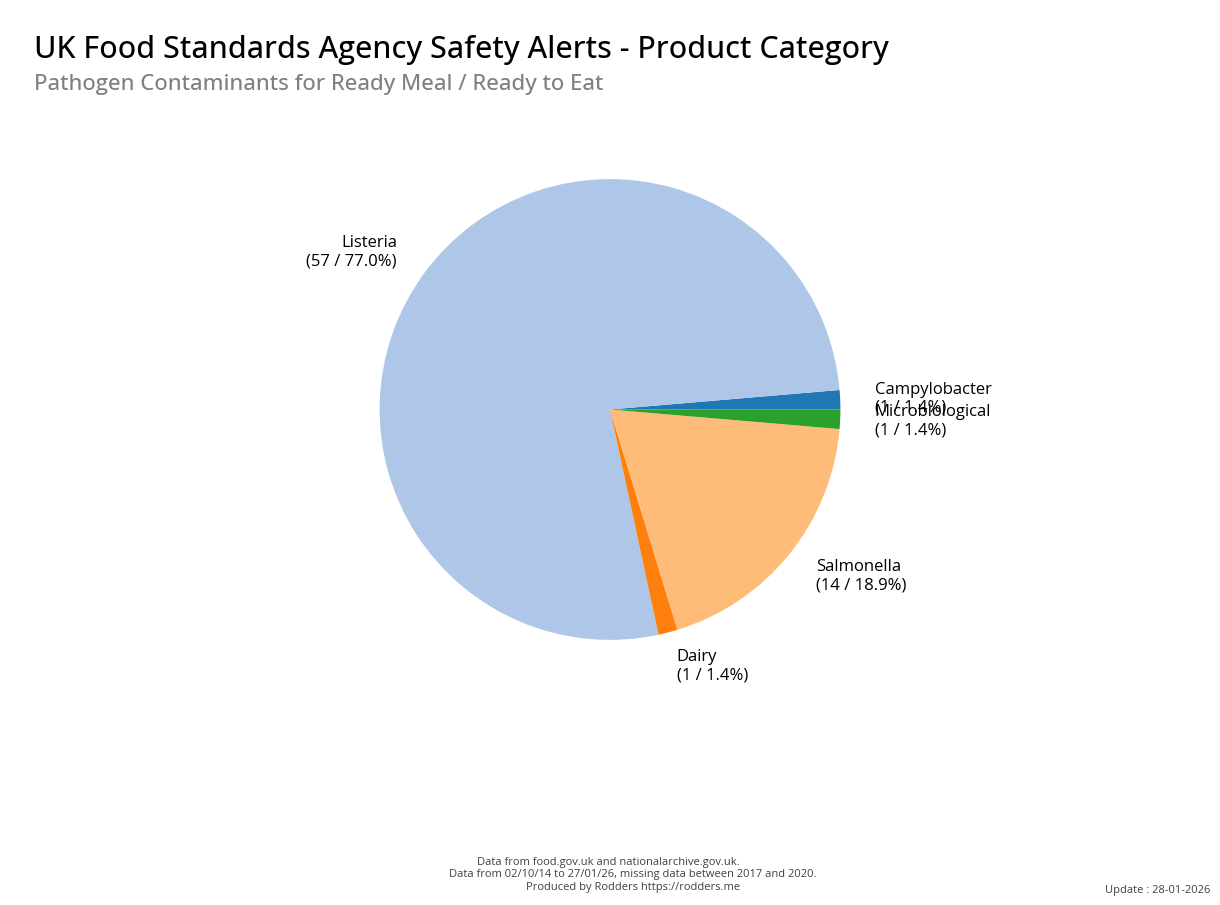
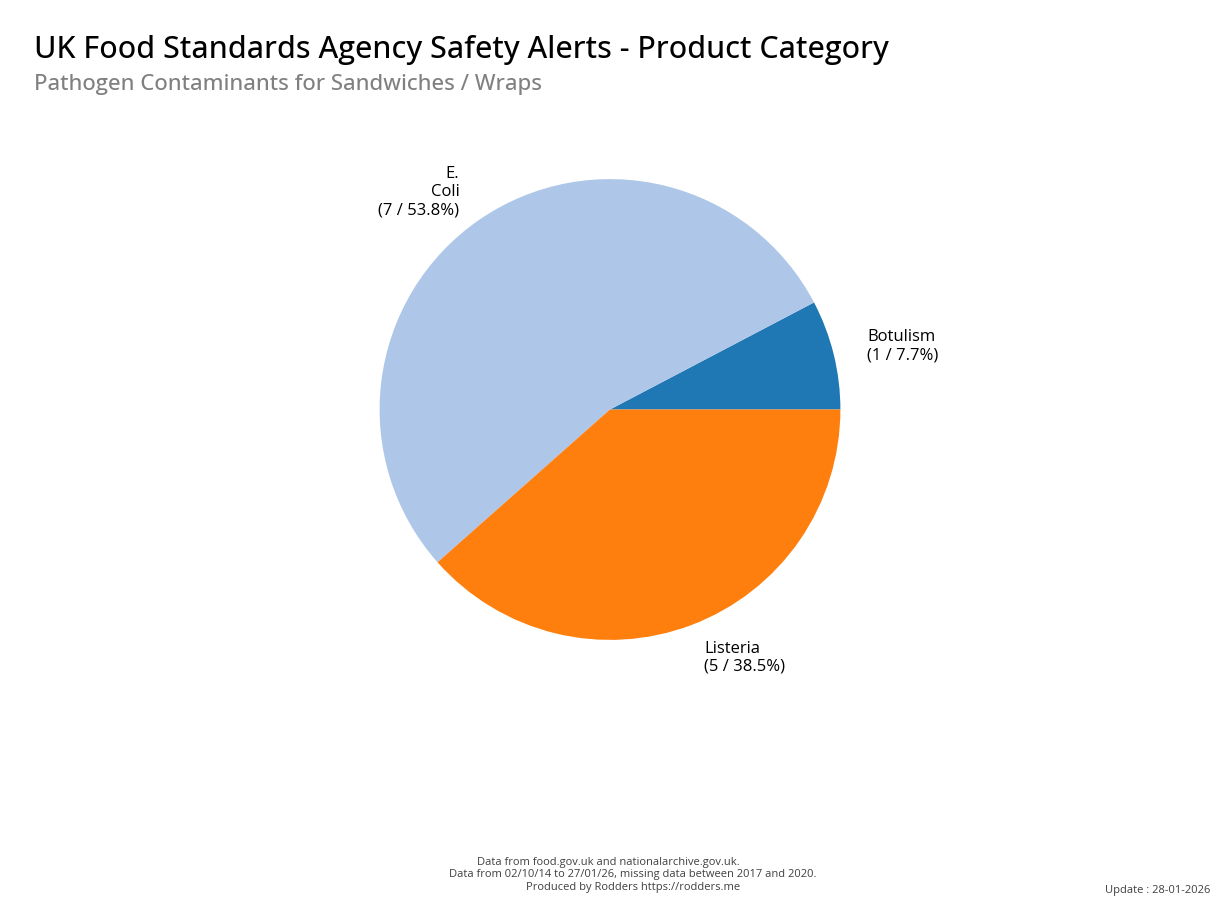
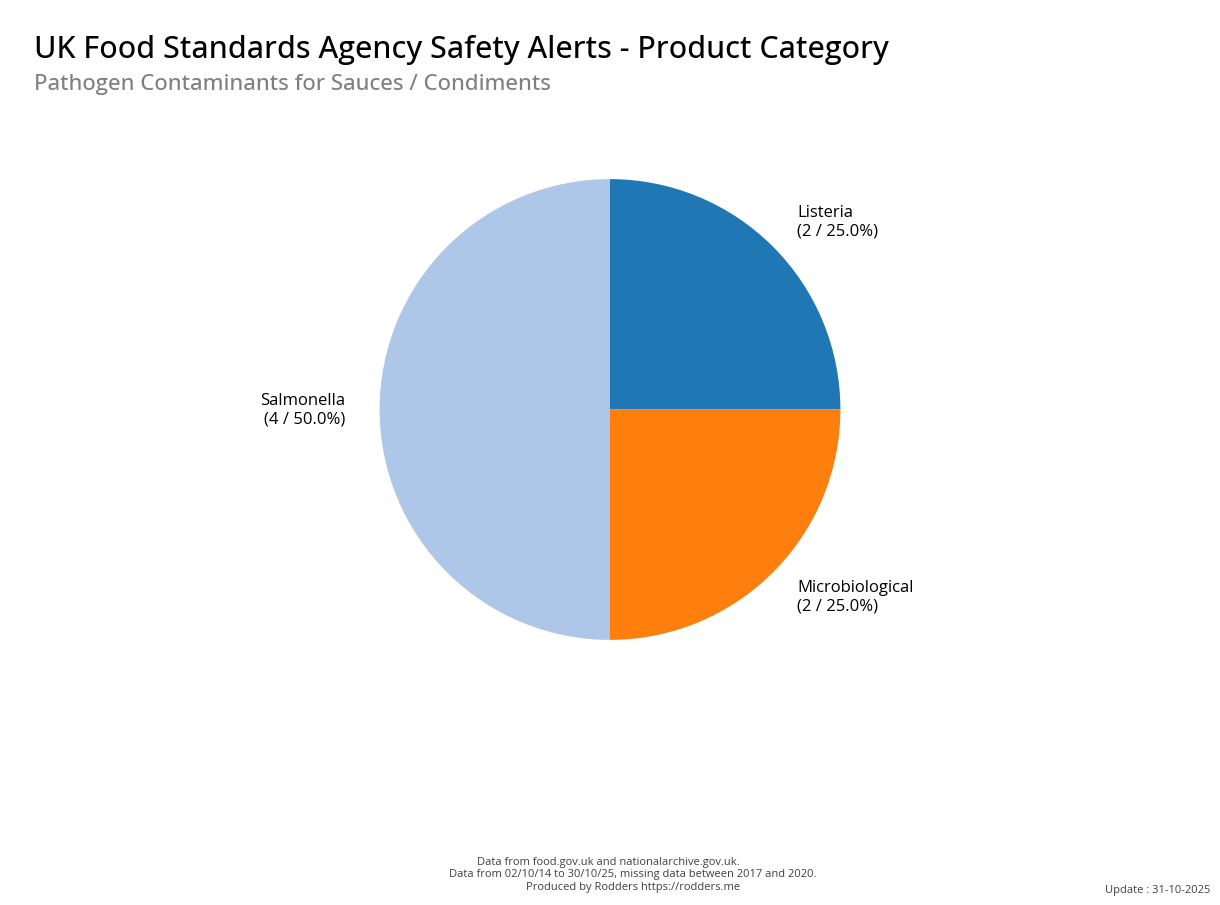
A Taste of Trouble: Common Food Contaminants by Product Category
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Top
Summary
Food Safety Alerts for Pathogenic contaminations account 23% of all safety alerts issued by the FSA.
There has been a measurable increase in the number of pathogen safety alerts in 2024 (so far) compared to the previous few years.
Salmonella, Listeria, Clostridium botulinum, E.Coli are the most common pathogenic food contaminants accounting for 88% of all pathogen safety alerts
| Pathogen | count | total |
|---|---|---|
| Salmonella | 80 | 41.6% |
| Listeria | 57 | 29.7% |
| Clostridium botulinum | 17 | 8.9% |
| E.Coli | 16 | 8.3% |
| Microbiological | 10 | 5.2% |
| Cronobacter sakazakii | 4 | 2.0% |
| Hepatitis A | 3 | 1.6% |
| Norovirus | 2 | 1.0% |
| Rhizopus oryzae | 1 | 0.5% |
| Food Poisoning | 1 | 0.5% |
| Campylobacter | 1 | 0.5% |
Top